Page 11 - ITPS-8-1
P. 11
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences Image-assisted personalized interventions
pair consents an adaptive control for a procedure when recommended medical prescriptions to meet the safety
functioning. Figure 2 summarizes the topographies features related to imaging and interventional actions
62
of a DT for monitoring an image-guided intervention for the intervention concerned. Such planning allows
procedure. confirming the smooth running of the intervention and
the possible adaptations required for the medical protocol
Note that the DT concept is progressively incorporating
the healthcare sphere exploiting virtual replicas of practiced. Therefore, the real (with patient) image-guided
bodily individuals that go further than a static situation intervention could be performed under good conditions,
incorporating the dynamic conduct of a real living which could be achieved through an image-assisted
collaborative environment, as illustrated in Figure 1, under
tissues entity, many examples have been published in this the supervision of medical staff, or prospectively through
intention, see for instance. 63-73 As the healthcare sector is an autonomous DT monitoring procedure with involved
gradually exploring the use of DTs, successful proofs of staff (in the loop).
concept in various sectors suggest that, if fully realized,
DTs could transform connected care, lifestyle, health, 4.1. Physical and virtual phantoms
and chronic disease management in the future. However,
recognition of the vast capacity of DTs in health care may Physical and digital phantoms, discussed in the previous
likely be slowed by hesitation challenges. section, represent living tissues on both sides of the
DT. A major problem with both choices lies in the way
4. Planning of personalized and medical of tissue representation. Considering that biological
rulings properties allow the erection of these phantoms with
static behavior, such a static representation could
The concept of DT discussed in the previous section could be suitable for specific parts of body tissues and for
be used in planning a fictive intervention without a patient. particular demands. Nevertheless, as mentioned earlier,
In this case, we monitor the fully imaging-assisted robotic these phantoms should represent real body tissues
intervention procedure, including the scanner, the robot, with reasonable biological properties. In general, the
and the tissue (phantom). This physical phantom of the mechanical behavior related to the deformation and
tissue part of interest will be incorporated into the real displacement of living soft tissues, irrigated by fluids
physical side of the DT. Similarly, the virtual model side allowing their functioning, corresponds to an exhibition
of the DT involving the intervention procedure model will of a complex dynamic behaviour. 74-78 Such a complex
include a digital phantom replica of the physical one. This tissue behavior requires actually evaluated constitutive
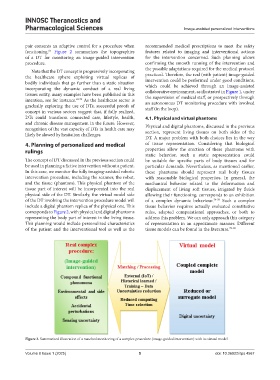
corresponds to Figure 2, with physical and digital phantoms rules, adapted computational approaches, or both to
representing the body part of interest in the living tissue. address this problem. We can only approach this category
This planning would include personalized characteristics of representation in an approximate manner. Different
of the patient and the interventional tool as well as the tissue models can be found in the literature. 79-82
Figure 2. Summarized illustration of a matched monitoring of a complex procedure (image-guided intervention) with its virtual model
Volume 8 Issue 1 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/itps.4567