Page 29 - JCAU-7-1
P. 29
Journal of Chinese
Architecture and Urbanism Spatial syntax of temple heritage
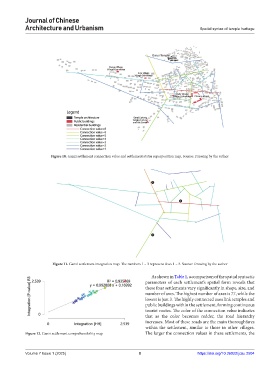
Figure 10. Ganzi settlement connection value and settlement status superposition map. Source: Drawing by the author
Figure 11. Ganzi settlement integration map. The numbers 1 – 3 represent Axes 1 – 3. Source: Drawing by the author
As shown in Table 1, a comparison of the spatial syntactic
parameters of each settlement’s spatial form reveals that
these four settlements vary significantly in shape, size, and
number of axes. The highest number of axes is 77, while the
lowest is just 3. The highly connected axes link temples and
public buildings within the settlement, forming continuous
tourist routes. The color of the connection value indicates
that as the color becomes redder, the road hierarchy
increases. Most of these roads are the main thoroughfares
within the settlement, similar to those in other villages.
Figure 12. Ganzi settlement comprehensibility map The larger the connection values in these settlements, the
Volume 7 Issue 1 (2025) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/jcau.2504