Page 97 - JCTR-11-5
P. 97
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research ROCK inhibition in chronic rejection
A B C
D E F
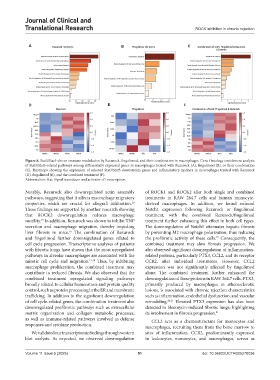
Figure 8. Stat3/Stat5-driven immune modulation by Rezurock, fingolimod, and their combination in macrophages. Gene Ontology enrichment analysis
of Stat3/Stat5-related pathways among differentially expressed genes in macrophages treated with Rezurock (A), fingolimod (B), or their combination
(C). Heatmaps showing the expression of selected Stat3/Stat5 downstream genes and inflammatory markers in macrophages treated with Rezurock
(D), fingolimod (E), and the combined treatment (F).
Abbreviation: Stat: Signal transducer and activator of transcription.
Notably, Rezurock also downregulated actin assembly of ROCK1 and ROCK2 after both single and combined
pathways, suggesting that it affects macrophage migratory treatments in RAW 264.7 cells and human monocyte-
properties, which are crucial for allograft infiltration. derived macrophages. In addition, we found reduced
10
These findings are supported by another research showing Notch1 expression following Rezurock or fingolimod
that ROCK2 downregulation reduces macrophage treatment, with the combined Rezurock/fingolimod
15
motility. In addition, Rezurock was shown to inhibit TNF treatment further enhancing this effect in both cell types.
secretion and macrophage migration, thereby impeding The downregulation of Notch1 attenuates hepatic fibrosis
liver fibrosis in mice. The combination of Rezurock by preventing M2 macrophage polarization, thus reducing
16
and fingolimod further downregulated genes related to the profibrotic activity of these cells. Consequently, the
19
cell cycle progression. Transcriptome analyses of patients combined treatment may slow fibrosis progression. We
with fibrotic lungs have shown that the most upregulated also observed significant downregulation of inflammation-
pathways in alveolar macrophages are associated with the related proteins, particularly PTX3, CCL2, and its receptor
mitotic cell cycle and migration. 17,18 Thus, by inhibiting CCR2, after individual treatments. However, CCL2
macrophage proliferation, the combined treatment may expression was not significantly affected by fingolimod
contribute to reduced fibrosis. We also observed that the alone. The combined treatment further enhanced the
combined treatment upregulated signaling pathways downregulation of these proteins in RAW 264.7 cells. PTX3,
broadly related to cellular homeostasis and protein quality primarily produced by macrophages in atherosclerotic
control, such as protein processing in the ER and membrane lesions, is associated with chronic rejection characteristics
trafficking. In addition to the significant downregulation such as inflammation, endothelial dysfunction, and vascular
of cell cycle-related genes, the combination treatment also remodeling. 20,21 Elevated PTX3 expression has also been
downregulated profibrotic pathways such as extracellular detected in bleomycin-induced fibrotic lungs, highlighting
matrix organization and collagen metabolic processes, its involvement in fibrosis progression. 21
as well as immune-related pathways involved in defense CCL2 acts as a chemoattractant for monocytes and
responses and cytokine production. macrophages, recruiting them from the bone marrow to
We validated our transcriptomic findings through western sites of inflammation. CCR2, predominantly expressed
blot analysis. As expected, we observed downregulation in leukocytes, monocytes, and macrophages, serves as
Volume 11 Issue 5 (2025) 91 doi: 10.36922/JCTR025270036