Page 95 - JCTR-11-5
P. 95
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research ROCK inhibition in chronic rejection
A B C D
G H
E F
J K
I
L M
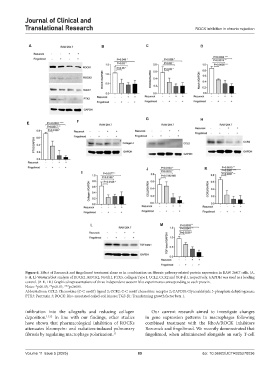
Figure 6. Effect of Rezurock and fingolimod treatment alone or in combination on fibrosis pathway-related protein expression in RAW 264.7 cells. (A,
F-H, L) Western blot analysis of ROCK1, ROCK2, Notch1, PTX3, collagen Type I, CCL2, CCR2 and TGF-β1, respectively. GAPDH was used as a loading
control. (B-E, I-K) Graphical representations of three independent western blot experiments corresponding to each protein.
Notes: *p≤0.05; **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.001.
Abbreviations: CCL2: Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2; CCR2: C-C motif chemokine receptor 2; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase;
PTX3: Pentraxin 3; ROCK: Rho-associated coiled-coil kinase; TGF-β1: Transforming growth factor beta 1.
infiltration into the allografts and reducing collagen Our current research aimed to investigate changes
deposition. 11,12 In line with our findings, other studies in gene expression patterns in macrophages following
have shown that pharmacological inhibition of ROCKs combined treatment with the RhoA/ROCK inhibitors
attenuates bleomycin- and radiation-induced pulmonary Rezurock and fingolimod. We recently demonstrated that
fibrosis by regulating macrophage polarization. 13 fingolimod, when administered alongside an early T-cell
Volume 11 Issue 5 (2025) 89 doi: 10.36922/JCTR025270036