Page 93 - JCTR-11-5
P. 93
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research ROCK inhibition in chronic rejection
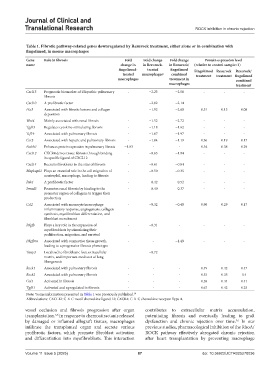
Table 1. Fibrotic pathway‑related genes downregulated by Rezurock treatment, either alone or in combination with
fingolimod, in mouse macrophages
Gene Role in fibrosis Fold Fold change Fold change Protein expression level
name change in in Rezurock‑ in Rezurock/ (relative to control sample=1)
fingolimod‑ treated fingolimod Fingolimod Rezurock Rezurock/
treated macrophages a combined treatment treatment fingolimod
macrophages treatment in combined
macrophages treatment
Cxcl13 Prognostic biomarker of idiopathic pulmonary - −2.23 −2.58 - - -
fibrosis
Cxcl10 A profibrotic factor - −2.02 −2.14 - - -
Ptx3 Associated with fibrotic lesions and collagen - −1.92 −2.68 0.51 0.15 0.08
deposition
Wnt4 Mainly associated with renal fibrosis - −1.52 −2.72 - - -
Tgfb3 Regulates cytokine-stimulating fibrosis - −1.18 −1.62 - - -
Tcf19 Associated with pulmonary fibrosis - −1.07 −1.97 - - -
Ccr2 Associated with hepatic and pulmonary fibrosis - −1.04 −1.19 0.36 0.19 0.17
Notch1 Enhances protein expression in pulmonary fibrosis −1.03 - - 0.54 0.38 0.29
Cxcl12 CXCR4 drives tissue fibrosis through binding - −0.63 −1.94 - - -
its specific ligand of CXCL12
Cxcl14 Recruits fibroblasts to the sites of fibrosis - −0.61 −0.84 - - -
Mapkapk2 Plays an essential role in the cell migration of - −0.50 −0.35 - - -
neutrophil, macrophage, leading to fibrosis
Pak1 A profibrotic factor - −0.42 −0.52 - - -
Smad3 Promotes renal fibrosis by binding to the - −0.40 −0.37 - - -
promoter region of collagens to trigger their
production
Ccl2 Associated with monocyte/macrophage - −0.32 −0.48 0.96 0.29 0.17
inflammatory response, angiogenesis, collagen
synthesis, myofibroblast differentiation, and
fibroblast recruitment
Pdgfb Plays a key role in the expansion of - −0.31 - - - -
myofibroblasts by stimulating their
proliferation, migration, and survival
Pdgfbra Associated with connective tissue growth, - - −1.49 - - -
leading to a progressive fibrosis phenotype
Timp3 Localized to fibroblastic foci, extracellular - −0.72 - - - -
matrix, and important mediator of lung
fibrogenesis
Rock1 Associated with pulmonary fibrosis - - - 0.49 0.42 0.47
Rock2 Associated with pulmonary fibrosis - - - 0.53 0.35 0.4
Col1 Activated in fibrosis - - - 0.38 0.44 0.41
Tgfb1 Activated and upregulated in fibrosis - - - 0.67 0.42 0.25
Note: Some information presented in Table 1 was previously published. 10
a
Abbreviations: CXCL12: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12; CXCR4: C-X-C chemokine receptor Type 4.
vessel occlusion and fibrosis progression after organ contributes to extracellular matrix accumulation,
transplantation. In response to chemoattractants released potentiating fibrosis and eventually leading to graft
5,6
by damaged or inflamed allograft tissues, macrophages dysfunction and chronic rejection over time. In our
5,6
infiltrate the transplanted organ and secrete various previous studies, pharmacological inhibition of the RhoA/
profibrotic factors, which promote fibroblast activation ROCK pathway effectively abrogated chronic rejection
and differentiation into myofibroblasts. This interaction after heart transplantation by preventing macrophage
Volume 11 Issue 5 (2025) 87 doi: 10.36922/JCTR025270036