Page 55 - JCTR-9-6
P. 55
Mustahsan et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2023; 9(6): 414-422 419
A B
Figure 5. (A and B) Results of mean values of average red pixel intensity (orange) in Alizarin red staining for calcium deposits and mean value for
average dark pixel intensity in Von Kossa staining (blue) for mineralization on scaffolds’ surface (n = 10). Error bars represent the standard deviation.
A B
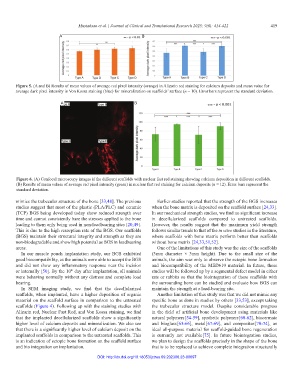
Figure 6. (A) Confocal microscopy images if the different scaffolds with nuclear fast red staining showing calcium deposition in different scaffolds.
(B) Results of mean values of average red pixel intensity (green) in nuclear fast red staining for calcium deposits (n = 12). Error bars represent the
standard deviation.
mimics the trabecular structure of the bone [33,48]. The previous Earlier studies reported that the strength of the BGS increases
studies suggest that most of the plastic (PLA/PLC) and ceramic when the bone matrix is deposited on the scaffold surface [24,33].
(TCP) BGS being developed today show reduced strength over In our mechanical strength studies, we find no significant increase
time and cannot consistently bare the stresses applied to the bone in decellularized scaffolds compared to untreated scaffolds.
leading to them only being used in non-loadbearing sites [20,49]. However, the results suggest that the maximum yield strength
This is due to the high resorption rate of the BGS. Our scaffolds follows similar trends to that of the in vitro studies in the literature,
(BGS) maintain their structural integrity and strength as they are where scaffolds with bone matrix perform better than scaffolds
non-biodegradable and show high potential as BGS in loadbearing without bone matrix [24,33,51,52].
areas. One of the limitations of this study was the size of the scaffolds
In our muscle pouch implantation study, our BGS exhibited (3mm diameter × 3mm height). Due to the small size of the
good biocompatibility, as the animals were able to accept the BGS animals, the aim was only to observe the ectopic bone formation
and did not show any inflammatory response near the incision and biocompatibility of the MED610 material. In future, these
or internally [50]. By the 10 day after implantation, all animals studies will be followed up by a segmental defect model in either
th
were behaving normally without any distress and complete load rats or rabbits so that the biointegration of these scaffolds with
bearing. the surrounding bone can be studied and evaluate how BGS can
In SEM imaging study, we find that the decellularized maintain the strength at a load-bearing site.
scaffolds, when implanted, have a higher deposition of organic Another limitation of this study was that we did not mimic any
material on the scaffold surface in comparison to the untreated specific bone as done in studies by others [33,53], except taking
scaffolds (Figure 4). Following up with the staining studies with the trabecular structure model. Despite considerable progress
Alizarin red, Nuclear Fast Red, and Von Kossa staining, we find in the field of artificial bone development using materials like
that the implanted decellularized scaffolds show a significantly natural polymers [54-59], synthetic polymers [60-62], biocermaic
higher level of calcium deposits and mineralization. We also see and bioglass [63-66], metal [67-69], and composites [70-74], an
that there is a significantly higher level of calcium deposit on the ideal all-purpose material for scaffold-guided bone regeneration
implanted scaffolds in comparison to the untreated scaffolds. This is currently not available [75]. In future biointegration studies,
is an indication of ectopic bone formation on the scaffold surface we plan to design the scaffolds precisely in the shape of the bone
and bio integration on implantation. that is to be replaced to achieve complete integration structurally
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18053/jctres.09.202306.23-00097