Page 85 - MI-2-3
P. 85
Microbes & Immunity Carotene and immunity to COVID-19 vaccine
A B A B
C D
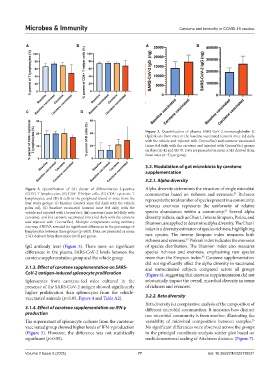
Figure 3. Quantification of plasma SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulin G
(IgG) levels from mice in the baseline vaccinated (control mice fed daily
with the vehicle and injected with CoronaVac) and carotene vaccinated
(mice fed daily with the carotene and injected with CoronaVac) groups
on days (A) 42 and (B) 70. Data are presented as mean ± SD, derived from
three mice (n=3) per group.
3.2. Modulation of gut microbiota by carotene
supplementation
3.2.1. Alpha diversity
Figure 2. Quantification of (A) cluster of differentiation 3-positive Alpha diversity determines the structure of single microbial
(CD3 ) T lymphocytes, (B) CD4 T-helper cells, (C) CD8 cytotoxic T communities based on richness and evenness. Richness
+
25
+
+
lymphocytes, and (D) B cells in the peripheral blood of mice from the represents the total number of species present in a community,
four study groups: (i) baseline (control mice fed daily with the vehicle
palm oil), (ii) baseline vaccinated (control mice fed daily with the whereas evenness represents the uniformity of relative
25
vehicle and injected with CoronaVac), (iii) carotene (mice fed daily with species abundances within a community. Several alpha
carotene), and (iv) carotene vaccinated (mice fed daily with the carotene diversity indices, such as Chao1, Inverse Simpson, Pielou, and
and injected with CoronaVac). Multiple comparisons using ordinary Shannon, are applied to determine alpha diversity. The Chao1
one-way ANOVA revealed no significant differences in the percentage of index is a diversity estimator of species richness, highlighting
lymphocytes between these groups (p>0.05). Data are presented as mean
± SD, derived from three mice (n=3) per group. rare species. The inverse Simpson index measures both
richness and evenness. Pielou’s index indicates the evenness
25
IgG antibody level (Figure 3). There were no significant of species distribution. The Shannon index also measures
differences in the plasma SARS-CoV-2 levels between the species richness and evenness, emphasizing rare species
carotene supplementation group and the vehicle group. more than the Simpson index. Carotene supplementation
25
did not significantly affect the alpha diversity in vaccinated
3.1.3. Effect of carotene supplementation on SARS- and unvaccinated subjects compared across all groups
CoV-2 antigen-induced splenocyte proliferation (Figure 6), suggesting that carotene supplementation did not
Splenocytes from carotene-fed mice cultured in the substantially impact the overall microbial diversity in terms
presence of the SARS-CoV-2 antigen showed significantly of richness and evenness.
higher proliferation than splenocytes from the vehicle-
vaccinated animals (p<0.05, Figure 4 and Table A2). 3.2.2. Beta diversity
Beta diversity is a comparative analysis of the composition of
3.1.4. Effect of carotene supplementation on IFN-γ different microbial communities. It measures how distinct
production one microbial community is from another, illustrating the
The supernatant of splenocyte cultures from the carotene- variability of microbial composition between samples.
25
vaccinated group showed higher levels of IFN-γ production No significant differences were observed across the groups
(Figure 5). However, the difference was not statistically in the principal coordinate analysis scatter plot based on
significant (p>0.05). multidimensional scaling of Aitchison distance (Figure 7).
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 77 doi: 10.36922/MI025110021