Page 89 - MI-2-3
P. 89
Microbes & Immunity Carotene and immunity to COVID-19 vaccine
A B
C
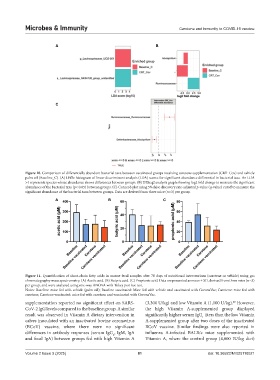
Figure 10. Comparison of differentially abundant bacterial taxa between vaccinated groups receiving carotene supplementation (CRT_Cov) and vehicle
palm oil (Baseline_C). (A) LEfSe histogram of linear discriminant analysis (LDA) scores for significant abundance differential in bacterial taxa. An LDA
>4 represents species whose abundance shows differences between groups. (B) DESeq2 analysis graph showing log2 fold change to measure the significant
abundance of the bacterial taxa (p< 0.05) between groups. (C) Corncob plot using 5% false discovery rate-adjusted p-value (q-value) cutoff to measure the
significant abundance of the bacterial taxa between groups. Data are derived from three mice (n=3) per group.
A B C
Figure 11. Quantification of short-chain fatty acids in mouse fecal samples after 70 days of nutritional interventions (carotene or vehicle) using gas
chromatography-mass spectrometry. (A) Acetic acid. (B) Butyric acid. (C) Propionic acid. Data are presented as mean ± SD, derived from three mice (n=3)
per group, and were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test.
Notes: Baseline: mice fed with vehicle (palm oil); Baseline vaccinated: Mice fed with vehicle and vaccinated with CoronaVac; Carotene: mice fed with
carotene; Carotene vaccinated: mice fed with carotene and vaccinated with CoronaVac.
supplementation reported no significant effect on SARS- (3,300 U/kg) and low Vitamin A (1,100 U/kg). However,
29
CoV-2 IgG levels compared to the baseline group. A similar the high Vitamin A-supplemented group displayed
result was observed in Vitamin A dietary intervention in significantly higher serum IgG titers than the low Vitamin
1
calves inoculated with an inactivated bovine coronavirus A-supplemented group after two doses of the inactivated
(BCoV) vaccine, where there were no significant BCoV vaccine. Similar findings were also reported in
differences in antibody responses (serum IgG , IgM, IgA influenza A-infected BALB/c mice supplemented with
2
and fecal IgA) between groups fed with high Vitamin A Vitamin A, where the control group (4,000 IU/kg diet)
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 81 doi: 10.36922/MI025110021