Page 54 - MSAM-1-3
P. 54
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Characterization of TPMS structures
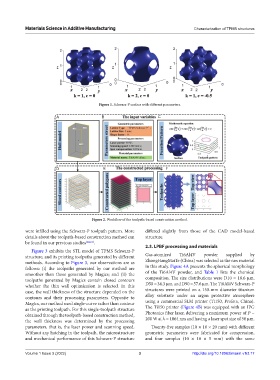
Figure 1. Schwarz-P surface with different parameters.
A B C
D E F
Figure 2. Workflow of the toolpath-based construction method.
were infilled using the Schwarz-P toolpath pattern. More differed slightly from those of the CAD model-based
details about the toolpath-based construction method can structure.
be found in our previous studies [20,21] .
2.3. LPBF processing and materials
Figure 3 exhibits the STL model of TPMS Schwarz-P
structure, and its printing toolpaths generated by different Gas-atomized Ti6Al4V powder supplied by
methods. According to Figure 3, our observations are as ZhongHangMaiTe (China) was selected as the raw material
follows: (i) the toolpaths generated by our method are in this study. Figure 4A presents the spherical morphology
smoother than those generated by Magics; and (ii) the of the Ti6Al4V powder, and Table 1 lists the chemical
toolpaths generated by Magics contain closed contours composition. The size distributions were D10 = 18.6 μm,
whether the thin wall optimization is selected. In this D50 = 34.3 μm, and D90 = 57.6 μm. The Ti6Al4V Schwarz-P
case, the wall thickness of the structure depended on the structures were printed on a 150-mm diameter titanium
contours and their processing parameters. Opposite to alloy substrate under an argon protective atmosphere
Magics, our method used single-curve rather than contour using a commercial SLM printer (Ti150, Profeta, China).
as the printing toolpath. For this single-toolpath structure The Ti150 printer (Figure 4B) was equipped with an IPG
obtained through the toolpath-based construction method, Photonics fiber laser, delivering a maximum power of P =
the wall thickness was determined by the processing 200 W at λ = 1064 nm and having a laser spot size of 50 μm.
parameters, that is, the laser power and scanning speed. Twenty-five samples (10 × 10 × 20 mm) with different
Without any hatching in the toolpath, the microstructure geometric parameters were fabricated for compression,
and mechanical performance of this Schwarz-P structure and four samples (10 × 10 × 5 mm) with the same
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2022) 3 http://doi.org/10.18063/msam.v1i3.17