Page 71 - MSAM-1-4
P. 71
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Survey of AM reviews
polyester (TPC). In general, support removal and post-
processing may be needed after fabrication .
[9]
2.2. Powder bed fusion
Powder bed fusion is another AM process. Typically,
powder bed fusion selectively melts the powder in the tank
[10]
using an energy beam (laser or electron) . After scanning
and finishing one layer of powder, the rolling mechanism
helps spread the next layer of the powder. Then, the next
layer is scanned, melted, and fused, until the entire part
is completed. In the mid-1980s, Deckard and Beaman
developed the polymer powder bed fusion technology, which
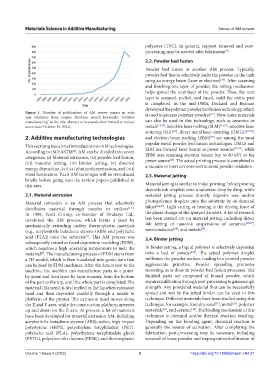
Figure 1. Number of publications of AM review papers in each is used to process polymer powders . Now, more materials
[11]
year (statistics from Scopus database; search keywords: “additive
manufacturing” in the title, abstract or keywords, then limited to review; can also be used in this technology, such as ceramics or
access date: October 19, 2022). metals [12,13] . Selective laser melting (SLM) [14,15] , selective laser
sintering (SLS) , direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) [17,18] ,
[16]
2. Additive manufacturing technologies and electron beam melting (EBM) are among the most
[19]
popular metal powder bed fusion technologies. DMLS and
This section gives a brief introduction on AM technologies. SLM use focused laser beams as power sources [20-22] , while
According to ISO/ASTM , AM can be divided into seven EBM uses scanning electron beams (up to 60 kV) as the
[2]
categories: (i) Material extrusion, (ii) powder bed fusion, [23]
(iii) material jetting, (iv) binder jetting, (v) directed power source . The actual printing process is completed in
energy deposition, (vi) vat photopolymerization, and (vii) a vacuum or inert environment to avoid powder oxidation.
sheet lamination. Each AM technique will be introduced 2.3. Material jetting
briefly before going into the review papers published in
this area. Material jetting is similar to inkjet printing. Inkjet printing
deposits ink droplets onto a substrate drop by drop, while
2.1. Material extrusion material jetting process directly deposits wax and/or
Material extrusion is an AM process that selectively photopolymer droplets onto the substrate by on-demand
[24,25]
distributes material through nozzles or orifices [3-6] . inkjet . Light curing or heating is the driving force of
In 1988, Scott Crump, co-founder of Stratasys Ltd., the phase change of the sprayed droplets. A lot of research
developed the AM process, which forms a layer by has been carried out on material jetting, including direct
mechanically extruding molten thermoplastic materials ink jetting of nanoink suspensions of ceramics [26,27] ,
[28]
[29]
(e.g., acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and polylactic semiconductor , and metals .
acid (PLA)) onto the substrate . This AM process was 2.4. Binder jetting
[7]
subsequently coined as fused deposition modeling (FDM),
which requires a high operating temperature to melt the In binder jetting, a liquid polymer is selectively deposited
[30]
material . The manufacturing process of FDM starts from onto a bed of powder . The jetted polymer droplet
[8]
a 3D model, which is then translated into gcode data that infiltrates the powder surface, leading to a printed powder
can be read by FDM machines. After the data is sent to the agglomerate primitive. Powder spreading promotes
machine, the machine can manufacture parts in a point- recoating, as is done in powder bed fusion processes. The
by-point and then layer-by-layer manner, from the bottom finished parts are composed of bound powder, which
of the part to the top, until the whole part is completed. The requires infiltration through post-processing to gain enough
material (filament) is first melted in the liquefier/extrusion strength. Any powdered material that can be successfully
head and then deposited carefully through a nozzle to spread and wet by the jetted binder can be used in this
platform of the printer. The extrusion head moves along technique. Different materials have been studied using this
the X and Y axes, while the construction platform operates technique, for example, foundry sand , metal , polymer
[32]
[31]
[34]
[33]
up and down on the Z axis. At present, a lot of materials materials , and ceramic . The binding mechanism of this
have been developed for material extrusion AM, including technique is chemical and/or thermal reaction bonding.
acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS), nylon, high impact Depending on the bonding agent, chemical reaction is
polystyrene (HIPS), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), generally the source of activation. After completing the
polylactic acid (PLA), polyethylene terephthalate glycol fabrication, post-processing may be necessary, including
(PETG), polyether ether ketone (PEEK), and thermoplastic removal of loose powder and impregnation/infiltration of
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2022) 2 https://doi.org/10.18063/msam.v1i4.21