Page 43 - MSAM-2-1
P. 43
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Data imputation strategies of PBF Ti64
melting layers of powder to form functional parts using microstructural changes, which can affect the mechanical
computer-aided design (CAD) software which allows for properties of the final product. Different processing
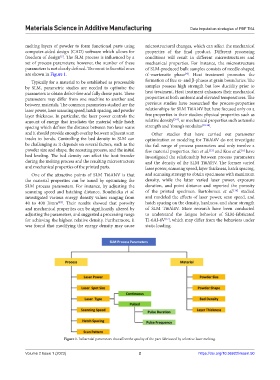
freedom of design . The SLM process is influenced by a conditions will result in different microstructures and
[2]
set of process parameters; however, the number of these mechanical properties. For instance, the microstructure
parameters is not clearly defined. The most influential ones of SLM-produced bulk samples consists of needle-shaped
are shown in Figure 1. α’-martensite phase . Heat treatment promotes the
[4]
Typically for a material to be established as processable formation of free α- and β-phases at grain boundaries. The
by SLM, parametric studies are needed to optimize the samples possess high strength but low ductility prior to
parameters to obtain defect-free and fully dense parts. These heat treatment. Heat treatment enhances their mechanical
parameters may differ from one machine to another and properties at both ambient and elevated temperatures. The
between materials. The common parameters studied are the previous studies have researched the process-properties
laser power, laser scanning speed, hatch spacing, and powder relationships for SLM Ti6Al4V but have focused only on a
layer thickness. In particular, the laser power controls the few properties in their studies: physical properties such as
amount of energy that irradiates the material while hatch relative density [5-9] , or mechanical properties such as tensile
spacing which defines the distance between two laser scans strength and Young’s modulus [10-14] .
and it should provide enough overlap between adjacent scan Other studies that have carried out parameter
tracks to bonds. Controlling the bed density in SLM can optimization or modeling for Ti6Al4V do not investigate
be challenging as it depends on several factors, such as the the full range of process parameters and only involve a
powder size and shape, the recoating process, and the initial few material properties. Sun et al. and Kuo et al. have
[6]
[15]
bed leveling. The bed density can affect the heat transfer investigated the relationship between process parameters
during the melting process and the resulting microstructure and the density of the SLM Ti6Al4V. The former varied
and mechanical properties of the printed parts. laser power, scanning speed, layer thickness, hatch spacing,
One of the attractive points of SLM Ti6Al4V is that and scanning strategy to obtain specimens with maximum
the material properties can be tuned by optimizing the density, while the latter varied laser power, exposure
SLM process parameters. For instance, by adjusting the duration, and point distance and reported the porosity
scanning speed and hatching distance, Roudnicka et al. of the printed specimen. Bartolomeu et al. studied
[16]
investigated various energy density values ranging from and modeled the effects of laser power, scan speed, and
40 to 400 J/mm . Their results showed that porosity hatch spacing on the density, hardness, and shear strength
3[3]
and mechanical properties can be significantly altered by of SLM Ti6Al4V. More research have been conducted
adjusting the parameters, and suggested a processing range to understand the fatigue behavior of SLM-fabricated
for achieving the highest relative density. Furthermore, it Ti-6Al-4V , which may differ from the behaviors under
[17]
was found that modifying the energy density may cause static loading.
Figure 1. Influential parameters that affect the quality of the part fabricated by selective laser melting.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 2 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.50