Page 69 - MSAM-2-4
P. 69
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Base shape generation for HAM
combinatorial optimization problems. It is a stochastic
optimization method that mimics natural evolution,
whereby individuals in each generation go through the
processes of crossover, mutation, and selection . During
[46]
the search, the branches can be randomly selected to form
a combination. Hence, this is a discrete optimization
problem since non-connected branches may be selected.
In the encoding, if a branch is selected, a digital value, 1,
is assigned; otherwise, another value, 0, is assigned. The
objective function is the whole volumes of the subparts
in a combination, which is randomly generated from the
original branches.
g
V n V i (I)
i0
where V is the Boolean union sum of selected subparts,
g
and V (i = 1, 2, 3…) is the volume of each subpart in
i
a generated combination. Theoretically, selecting all the
branches is the optimal solution, if we do not consider
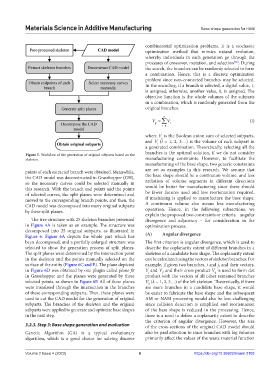
Figure 5. Workflow of the generation of original subparts based on the
skeleton. manufacturing constraints. However, to facilitate the
manufacturing of the base shape, two generic constraints
points of each extracted branch were obtained. Meanwhile, are set as examples in this research. We assume that
the CAD model was deconstructed in Grasshopper (GH), the base shape should be a continuum volume, and less
so the necessary curves could be selected manually in radiation of volume segments in different directions
this research. With the branch end points and the points would be better for manufacturing since there should
of selected curves, the split planes were determined and be fewer fixtures used and less reorientation required,
moved to the corresponding branch points, and then, the if machining is applied to manufacture the base shape.
CAD model was decomposed into many original subparts A continuum volume also means less manufacturing
by these split planes. operation. Hence, in the following subsections, we
explain the proposed two constraints or criteria – angular
The tree structure with 25 skeleton branches presented divergence and adjacency – for consideration in the
in Figure 4A is taken as an example. The structure was optimization process.
decomposed into 25 original subparts, as illustrated in
Figure 6. Figure 6A depicts the whole part which has (A) Angular divergence
been decomposed, and a partially enlarged structure was The first criterion is angular divergence, which is used to
selected to show the generation process of split planes. describe the coplanarity extent of different branches in a
The split planes were determined by the intersection point skeleton of a candidate base shape. The coplanarity extent
in the skeleton and the points manually selected on the can be calculated using the vectors of skeleton branches. For
surface of the entity (Figure 6C and E). The plane depicted example, if given two branches, i and j, and their vectors,
in Figure 6D was obtained by one plugin called plane fit V and V, and their cross product V is used to form dot
ij
j
i
in Grasshopper and the planes were generated by three product with the vectors of all other remained branches
selected points, as shown in Figure 6F. All of these planes V (k = 1, 2, 3…) of the left skeleton. Theoretically, if there
k
were translated through the intersection in the branches are more branches in a candidate base shape, it would
of these corresponding subparts. Then, these planes were be easier to fabricate the base shape and the subsequent
used to cut the CAD model for the generation of original AM or NAM processing would also be less challenging
subparts. The branches of the skeleton and the original since collision detection is simplified and reorientation
subparts were applied to generate and optimize base shapes of the base shape is reduced in the processing. Hence,
in the next step. there is a need to define a coplanarity extent to describe
the criterion of angular divergence. However, the size
3.2.3. Step 3: Base shape generation and evaluation of the cross-sections of the original CAD model should
Genetic Algorithm (GA) is a typical evolutionary also be paid attention to since branches with big volumes
algorithm, which is a good choice for solving discrete primarily affect the values of the waste material function
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.2103