Page 70 - MSAM-2-4
P. 70
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Base shape generation for HAM
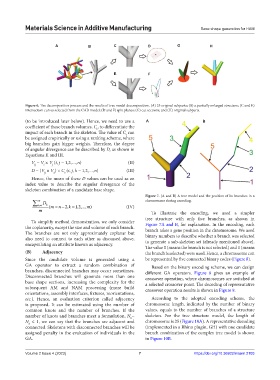
A B C D G H
E F
Figure 6. The decomposition process and the results of tree model decomposition. (A) 25 original subparts; (B) a partially enlarged structure; (C and E)
intersection curves selected from the CAD model; (D and F) split planes; (G) cut sections; and (H) original subparts.
(to be introduced later below). Hence, we need to use a A B
coefficient of these branch volumes, C , to differentiate the
v
impact of each branch in the skeleton. The value of C can
v
be assigned empirically or using a ranking scheme, where
big branches gain bigger weights. Therefore, the degree
of angular divergence can be described by D, as shown in
Equations II and III.
V = V × V (i, j = 1,2,…,n) (II)
ij
j
i
D = (V × V ) × C (i, j, k = 1,2,…,n) (III)
ij
k
v
Hence, the mean of these D values can be used as an
index value to describe the angular divergence of the
skeleton combination of a candidate base shape.
Figure 7. (A and B) A tree model and the position of its branches in a
m D k ( mn2, k 1 2,,..., m) (IV) chromosome during encoding.
k1
m To illustrate the encoding, we used a simpler
tree structure with only five branches, as shown in
To simplify method demonstration, we only consider Figure 7A and B, for explanation. In the encoding, each
the coplanarity, except the size and volume of each branch. branch takes a gene position in the chromosome. We used
The branches are not only approximately coplanar but binary numbers to describe whether a branch was selected
also need to connect to each other as discussed above, to generate a sub-skeleton set (already mentioned above).
encapsulating an attribute known as adjacency. The value 0 (means the branch is not selected) and 1 (means
(B) Adjacency the branch is selected) were used. Hence, a chromosome can
Since the candidate volume is generated using a be represented by five connected binary codes (Figure 8).
GA operator to extract a random combination of Based on the binary encoding scheme, we can design
branches, disconnected branches may occur sometimes. different GA operators. Figure 8 gives an example of
Disconnected branches will generate more than one crossover operation, where chromosomes are switched at
base shape sections, increasing the complexity for the a selected crossover point. The decoding of representative
subsequent AM and NAM processing (more build crossover operation results is shown in Figure 9.
orientations, assembly interfaces, fixtures, reorientations,
etc.). Hence, an evaluation criterion called adjacency According to the adopted encoding scheme, the
is proposed. It can be estimated using the number of chromosome length, indicated by the number of binary
common knots and the number of branches. If the values, equals to the number of branches of a structure
number of knots and branches meet a formulation, N − skeleton. For the tree structure model, the length of
k
N ≤ 1, we can say that the branches are adjacent and chromosome is 25 (Figure 10A). A representative decoding
b
connected. Skeletons with disconnected branches will be (implemented in a Rhino plugin, GH) with one candidate
assigned penalty in the evaluation of individuals in the branch combination of the complex tree model is shown
GA. in Figure 10B.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.2103