Page 71 - MSAM-2-4
P. 71
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Base shape generation for HAM
Figure 8. Chromosome and crossover operation.
A B C D
Figure 9. Decoding for the representative genetic algorithm chromosome
in Figure 8: (A) Parent 1; (B) Parent 2; (C) Child 1; and (D) Child 2.
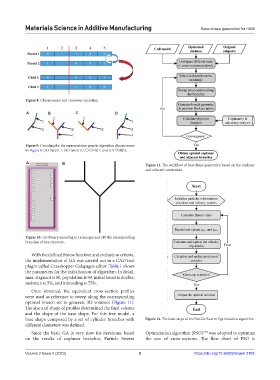
A B Figure 11. The workflow of base shape generation based on the coplanar
and adjacent constraints.
Figure 10. (A) Binary encoding in Galapagos and (B) the corresponding
branches of tree structure.
With the defined fitness function and evaluation criteria,
the implementation of GA was carried out in a CAD tool
plugin called Grasshopper Galapagos editor. Table 1 shows
the parameters for the initialization of algorithm. In detail,
max. stagnant is 50, population is 50, initial boost is double,
maintain is 5%, and inbreeding is 75%.
Once obtained, the equivalent cross-section profiles
were used as reference to sweep along the corresponding
optimal branch set to generate 3D volumes (Figure 11).
The size and shape of profiles determined the final volume
and the shape of the base shape. For this tree model, a
base shape composed by a set of cylinder branches with Figure 12. The basic steps of the Particle Swarm Optimization algorithm.
different diameters was defined.
Since the basic GA is very slow for iterations, based Optimization algorithm (PSO) was adopted to optimize
[47]
on the results of coplanar branches, Particle Swarm the size of cross-sections. The flow chart of PSO is
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2023) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.2103