Page 12 - MSAM-3-2
P. 12
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Functional materials for AM
robots capable of achieving complex behaviors through resulting in macroscopic deformation and exhibiting
the use of 3D-printed magnetically responsive soft intricate behavior. 41-43
materials (Table 2). Embedded magnetic filler particles A method has been developed to program complex
generate internal stress as they attempt to align with non-uniform magnetic domain patterns using permanent
the magnetic field under external magnetic influence, magnets or electromagnets on hard magnetic particles
A B C
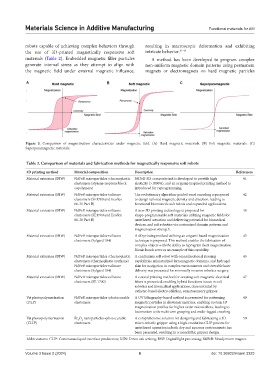
Figure 3. Comparison of magnetization characteristics under magnetic field. (A) Hard magnetic materials. (B) Soft magnetic materials. (C)
Superparamagnetic materials.
Table 2. Comparison of materials and fabrication methods for magnetically responsive soft robots
3D printing method Material composition Description References
Material extrusion (DIW) NdFeB microparticles+thermoplastic NdFeB-SIS composite ink is developed to provide high 41
elastomers (styrene-isoprene block elasticity (>1000%), and an origami-inspired printing method is
copolymers) introduced for reprogramming.
Material extrusion (DIW) NdFeB microparticles+silicone The evolutionary algorithm-guided voxel encoding is proposed 42
elastomers (SE1700 and Ecoflex to design tailored magnetic density and direction, leading to
00-30 Part B) functional biomimetic soft robots and expanded applications.
Material extrusion (DIW) NdFeB microparticles+silicone A new 3D printing technology is proposed for 44
elastomers (SE1700 and Ecoflex shape-programmable soft materials utilizing magnetic fields for
00-30 Part B) untethered actuation and delivering potential for biomedical
devices, and soft robotics via customized domain patterns and
magnetization strength.
Material extrusion (DIW) NdFeB microparticles+silicone A 4D printing method utilizing an origami-based magnetization 43
elastomers (Sylgard 184) technique is proposed. This method enables the fabrication of
complex objects with the ability to reprogram their magnetization.
Bionic hands serve as an example of this capability.
Material extrusion (DIW) NdFeB microparticles+thermoplastic A continuum soft robot with omnidirectional steering 45
elastomers (thermoplastic urethane) capabilities, miniaturized ferromagnetic domains, and hydrogel
NdFeB microparticles+silicone skin for navigation in complex environments and steerable laser
elastomers (Sylgard 184) delivery was presented for minimally invasive robotics surgery.
Material extrusion (DIW) NdFeB microparticles+silicone A coaxial printing method for creating soft-magnetic-electrical 47
elastomers (SE 1700) fibers is presented, enabling hybrid functions issues in soft
robotics and biomedical applications, demonstrated by
catheter-based electro-ablation, somatosensory gripper.
Vat photopolymerization NdFeB microparticles+photocurable A UV lithography-based method is presented for patterning 49
(DLP) elastomers magnetic particles in elastomer matrices, enabling custom 3D
magnetization profiles for higher-order microrobots, leading to
locomotion with multi-arm grasping and multi-legged crawling.
Vat photopolymerization Fe O nanoparticles+photocurable A comprehensive solution for designing and fabricating a 3D 50
3
4
(CLIP) elastomers micro-robotic gripper using a high-resolution CLIP process for
untethered operation in both dry and aqueous environments has
been presented, resulting in a monolithic gripper design.
Abbreviations: CLIP: Continuous liquid interface production; DIW: Direct ink writing; DLP: Digital light processing; NdFeB: Neodymium magnet.
Volume 3 Issue 2 (2024) 6 doi: 10.36922/msam.3323