Page 148 - MSAM-4-2
P. 148
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Bi-modal powder spreading behavior of ceramics
greater moisture retention, promoting cohesive clustering direction. The average packing density of the powder bed
and reducing their flowability, which causes them to settle was also 0.6900. This value shows a deviation of 1.45%
earlier in the spreading process. Furthermore, triboelectric from the packing density expected from the calculation of
charging from frictional contact with the spreader may create the powder fraction described in Section 2.2. This validates
electrostatic forces that selectively hinder or enhance the the powder fraction calculation. Furthermore, the packing
transport of specific particle sizes. These effects explain the density achieved in the simulation is within 10% of the
73
preferential deposition of smaller particles at the beginning previously reported studies. 74-76 The higher packing density
and larger particles toward the end of the spreading can arise from the smaller powder size and the bimodal
direction, as validated by simulation and experimental data. distribution of the powder size used in this study.
3.3. Powder bed packing density The packing density of the bimodal powder bed was
measured using cups to capture the powder from distinct
The packing density of the powder bed is an important locations on the powder bed. The placement of the density
aspect that influences the final quality of the final printed cups, the mean, and the standard deviation of the measured
part. After the powder spreading simulation, the Flow-3D packing density at each location are shown in Figure 6.
software (version 22.1.0.16, Flow Science, Santa Fe, NM, A total of 27 measurements were taken, with each X and
USA) was used to measure the packing density of the Y location having nine measurements. The average density
powder bed for the bimodal powder. To investigate the of the powder bed was 0.6651, which is below 4% error
spatial packing density from random powder generation compared to the simulation packing density of 0.6900. The
and spreading process, the packing density from all six average experimental packing density values are similar
sampling volumes was calculated along with the packing to those of the previous studies. 28,77 Previous studies have
density of the total powder bed. The packing density for shown that smaller powder can increase the packing
the start, middle, and end of the bed in the spreading 78,79
direction was 0.7000, 0.6900, and 0.6800, respectively. The density of the powder bed. The high experimental
packing density perpendicular to the spreading direction packing density can be attributed to the use of bimodal
was 0.6900 at all locations. Although there was a slight powder along with smaller particle sizes.
variation in packing density in the spreading direction, the When looking at the spatial packing density, interesting
variation was not observed perpendicular to the spreading patterns start to emerge. A statistical study was conducted
A B
C D
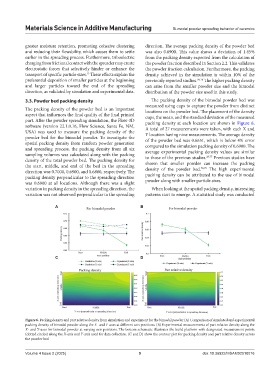
Figure 6. Packing density and part relative density from simulation and experiment for the bimodal powder (A) Comparison of simulated and experimental
packing density of bimodal powder along the X- and Y-axes at different axis positions. (B) Experimental measurements of part relative density along the
X- and Y-axes for bimodal powder at varying axis positions. The bottom schematic illustrates the build platform with designated measurement points
(dotted circles) along the X-axis and Y-axis used for data collection. (C and D) show the contour plot for packing density and part relative density across
the powder bed
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 9 doi: 10.36922/MSAM02510016