Page 88 - OR-1-2
P. 88
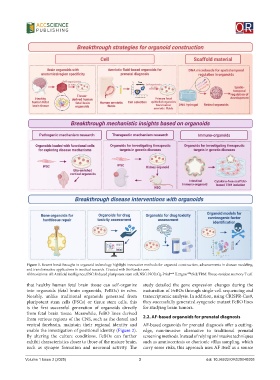
Figure 1. Recent breakthroughs in organoid technology highlight innovative methods for organoid construction, advancements in disease modeling,
and transformative applications in medical research. Created with BioRender.com.
Abbreviations: AI: Artificial intelligence; iPSC: Induced pluripotent stem cell; NSG: NOD.Cg-Prkd cscid IL2rgtm 1Wjl /SzJ; TRM: Tissue-resident memory T cell.
that healthy human fetal brain tissue can self-organize study detailed the gene expression changes during the
into organoids (fetal brain organoids, FeBOs) in vitro. maturation of FeBOs through single-cell sequencing and
Notably, unlike traditional organoids generated from transcriptomic analysis. In addition, using CRISPR-Cas9,
pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) or tissue stem cells, this they successfully generated syngeneic mutant FeBO lines
is the first successful generation of organoids directly for studying brain tumors.
from fetal brain tissue. Meanwhile, FeBO lines derived
from various regions of the CNS, such as the dorsal and 2.2. AF-based organoids for prenatal diagnosis
ventral forebrain, maintain their regional identity and AF-based organoids for prenatal diagnosis offer a cutting-
enable the investigation of positional identity (Figure 2). edge, non-invasive alternative to traditional prenatal
By altering the culture conditions, FeBOs can further screening methods. Instead of relying on invasive techniques
exhibit characteristics closer to those of the mature brain, such as amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling, which
such as synapse formation and neuronal activity. The carry some risks, this approach uses AF itself as a source
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 3 doi: 10.36922/OR025040005