Page 89 - OR-1-2
P. 89
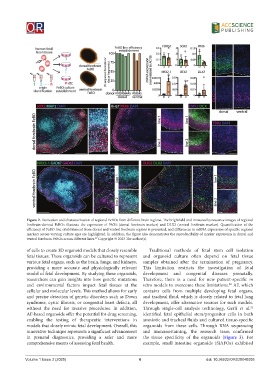
Figure 2. Derivation and characterization of regional FeBOs from different brain regions. The brightfield and immunofluorescence images of regional
forebrain-derived FeBOs illustrate the expression of PAX6 (dorsal forebrain marker) and DLX2 (ventral forebrain marker). Quantification of the
efficiency of FeBO line establishment from dorsal and ventral forebrain regions is presented, and differences in mRNA expression of specific regional
markers across varying culture ages are highlighted. In addition, the figure also demonstrates the reproducibility of marker expression in dorsal and
ventral forebrain FeBOs across different lines. Copyright © 2023 The author(s).
19
of cells to create 3D organoid models that closely resemble Traditional methods of fetal stem cell isolation
fetal tissues. These organoids can be cultured to represent and organoid culture often depend on fetal tissue
various fetal organs, such as the brain, lungs, and kidneys, samples obtained after the termination of pregnancy.
providing a more accurate and physiologically relevant This limitation restricts the investigation of fetal
model of fetal development. By studying these organoids, development and congenital diseases prenatally.
researchers can gain insights into how genetic mutations Therefore, there is a need for new patient-specific in
and environmental factors impact fetal tissues at the vitro models to overcome these limitations. AF, which
20
cellular and molecular levels. This method allows for early contains cells from multiple developing fetal organs,
and precise detection of genetic disorders such as Down and tracheal fluid, which is closely related to fetal lung
syndrome, cystic fibrosis, or congenital heart defects, all development, offer alternative sources for such models.
without the need for invasive procedures. In addition, Through single-cell analysis technology, Gerli et al.
21
AF-based organoids offer the potential for drug screening, identified fetal epithelial stem/progenitor cells in both
enabling the testing of therapeutic interventions in amniotic and tracheal fluids and cultured tissue-specific
models that closely mimic fetal development. Overall, this organoids from these cells. Through RNA sequencing
innovative technique represents a significant advancement and immunostaining, the research team confirmed
in prenatal diagnostics, providing a safer and more the tissue specificity of the organoids (Figure 3). For
comprehensive means of assessing fetal health. example, small intestine organoids (SiAFOs) exhibited
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 4 doi: 10.36922/OR025040005