Page 93 - OR-1-2
P. 93
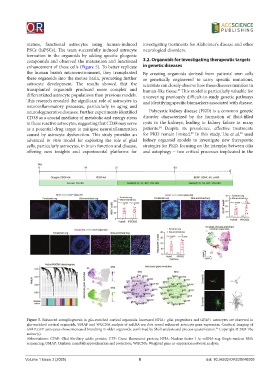
mature, functional astrocytes using human-induced investigating treatments for Alzheimer’s disease and other
PSCs (hiPSCs). The team successfully induced astrocyte neurological disorders.
formation in the organoids by adding specific gliogenic
compounds and observed the maturation and functional 3.2. Organoids for investigating therapeutic targets
enhancement of these cells (Figure 5). To better replicate in genetic diseases
the human brain’s microenvironment, they transplanted By creating organoids derived from patients’ own cells
these organoids into the mouse brain, promoting further or genetically engineered to carry specific mutations,
astrocyte development. The results showed that the scientists can closely observe how these diseases manifest in
transplanted organoids produced more complex and human-like tissue. This model is particularly valuable for
37
differentiated astrocyte populations than previous models. uncovering previously difficult-to-study genetic pathways
This research revealed the significant role of astrocytes in and identifying specific biomarkers associated with disease.
neuroinflammatory processes, particularly in aging and
neurodegenerative diseases. Further experiments identified Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is a common genetic
CD38 as a crucial mediator of metabolic and energy stress disorder characterized by the formation of fluid-filled
in these reactive astrocytes, suggesting that CD38 may serve cysts in the kidneys, leading to kidney failure in many
38
as a potential drug target to mitigate neuroinflammation patients. Despite its prevalence, effective treatments
40
caused by astrocyte dysfunction. This study provides an for PKD remain limited. In this study, Liu et al. used
39
advanced in vitro model for exploring the role of glial kidney organoid models to investigate new therapeutic
cells, particularly astrocytes, in brain function and disease, strategies for PKD, focusing on the interplay between cilia
offering new insights and experimental platforms for and autophagy – two critical processes implicated in the
Figure 5. Enhanced astrogliogenesis in glia-enriched cortical organoids. Increased NFIA+ glial progenitors and GFAP+ astrocytes are observed in
glia-enriched cortical organoids. UMAP and WGCNA analysis of snRNA-seq data reveal enhanced astrocyte gene expression. Confocal imaging of
GFAP::GFP astrocytes shows increased branching in older organoids, confirmed by Sholl analysis and process quantification. Copyright © 2024 The
36
author(s).
Abbreviations: GFAP: Glial fibrillary acidic protein; GFP: Green fluorescent protein; NFIA: Nuclear factor I A; snRNA-seq: Single-nucleus RNA
sequencing; UMAP: Uniform manifold approximation and projection; WGCNA: Weighted gene co-expression network analysis.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2025) 8 doi: 10.36922/OR025040005