Page 57 - TD-2-1
P. 57
Tumor Discovery LCP2 regulates melanoma progression
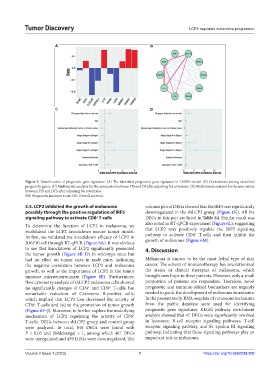
A B
C D
Figure 3. Identification of prognostic gene signature. (A) The identified prognostic gene signature in LASSO model. (B) Correlations among identified
prognostic genes. (C) Multivariate analysis for the association between PIS and OS after adjusting for covariates. (D) Multivariate analysis for the association
between PIS and DFS after adjusting for covariates.
PIS: Prognostic immune score; OS: Overall survival.
3.5. LCP2 inhibited the growth of melanoma volcano plot of DEGs showed that the IRF5 was significantly
possibly through the positive regulation of IRF5 downregulated in the shLCP2 group (Figure 6K). All the
signaling pathway to activate CD8 T-cells DEGs in this part are listed in Table S4. Similar result was
+
To determine the function of LCP2 in melanoma, we also noted in RT-qPCR experiment (Figure 6L), suggesting
established the LCP2 knockdown mouse tumor model. that LCP2 may positively regulate the IRF5 signaling
+
At first, we validated the knockdown efficacy of LCP2 in pathway to activate CD8 T-cells and then inhibit the
B16F10 cell through RT-qPCR (Figure 6A). It was obvious growth of melanoma (Figure 6M).
to see that knockdown of LCP2 significantly promoted 4. Discussion
the tumor growth (Figure 6B–D) in wild-type mice but
had no effect on tumor sizes in nude mice, indicating Melanoma is known to be the most lethal type of skin
the negative correlation between LCP2 and melanoma cancer. The advent of immunotherapy has revolutionized
growth, as well as the importance of LCP2 in the tumor the status of clinical therapies of melanoma, which
immune microenvironment (Figure 6E). Furthermore, brought new hope to these patients. However, only a small
flow cytometry analysis of shLCP2 melanoma cells showed proportion of patients are responders. Therefore, novel
no significantly changes of CD4 and CD8 T-cells, but prognostic and immune-related biomarkers are urgently
+
+
remarkable reduction of Granzyme B-positive cells, needed to guide the development of melanoma treatments.
which implied that LCP2 loss decreased the activity of In the present study, RNA-seq data of cutaneous melanoma
CD8 T-cells and led to the promotion of tumor growth from the public database were used for identifying
+
(Figure 6F–J). Moreover, to further explore the underlying prognostic gene signatures. KEGG pathway enrichment
mechanism of LCP2 regulating the activity of CD8 analysis showed that 47 DEGs were significantly involved
+
T-cells, DEGs between shLCP2 group and control group in lysosome, B-cell receptor signaling pathways, T-cell
were analyzed. In total, 846 DEGs were found with receptor signaling pathway, and Fc epsilon RI signaling
P < 0.05 and |foldchange| > 1, among which 407 DEGs pathway, indicating that these signaling pathways play an
were upregulated and 439 DEGs were downregulated. The important role in melanoma.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/td.308