Page 59 - TD-2-1
P. 59
Tumor Discovery LCP2 regulates melanoma progression
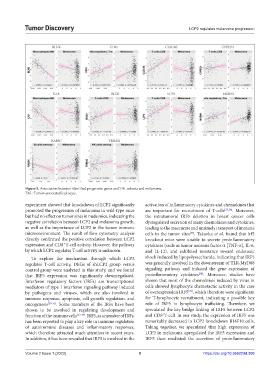
Figure 5. Association between identified prognostic genes and TAL subsets and melanoma.
TAL: Tumor-associated leukocyte.
experiment showed that knockdown of LCP2 significantly activation of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines that
promoted the progression of melanoma in wild-type mice are important for recruitment of T-cells [35,36] . Moreover,
but had no effect on tumor sizes in nude mice, indicating the the intratumoral IRF5 deletion in breast cancer cells
negative correlation between LCP2 and melanoma growth, dysregulated secretion of many chemokines and cytokines,
as well as the importance of LCP2 in the tumor immune leading to the inaccurate and untimely transport of immune
microenvironment. The result of flow cytometry analysis cells to the tumor sites . Takaoka et al. found that Irf5
[37]
directly confirmed the positive correlation between LCP2 knockout mice were unable to secrete proinflammatory
expression and CD8 T-cell activity. However, the pathway cytokines (such as tumor necrosis factor α [TNF-α], IL-6,
+
by which LCP2 regulates T-cell activity is unknown. and IL-12), and exhibited resistance toward endotoxic
To explore the mechanism through which LCP2 shock induced by lipopolysaccharide, indicating that IRF5
regulates T-cell activity, DEGs of shLCP2 group versus was generally involved in the downstream of TLR-MyD88
control group were analyzed in this study, and we found signaling pathway and induced the gene expression of
[38]
that IRF5 expression was significantly downregulated. proinflammatory cytokines . Moreover, studies have
Interferon regulatory factors (IRFs) are transcriptional shown that most of the chemokines induced by virus in
mediators of type 1 interferon signaling pathway induced cells showed lymphocyte chemotactic activity in the case
[35]
by pathogens and viruses, which are also involved in of overexpression IRF5 , which therefore were significant
immune response, apoptosis, cell growth regulation, and for T-lymphocyte recruitment, indicating a possible key
oncogenesis [29-31] . Some members of the IRFs have been role of IRF5 in lymphocyte trafficking. Therefore, we
shown to be involved in regulating development and speculated the key bridge linking of IRF5 between LCP2
+
function of the immune cells [32-34] . IRF5, as a member of IRFs, and CD8 T-cell. In our study, the expression of IRF5 was
has been reported to play a key role in immune regulation remarkably decreased in LCP2 knockdown B16F10 cells.
of autoimmune diseases and inflammatory responses, Taking together, we speculated that high expression of
which therefore attracted much attention in recent years. LCP2 in melanoma upregulated the IRF5 expression and
In addition, it has been revealed that IRF5 is involved in the IRF5 then mediated the secretion of proinflammatory
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/td.308