Page 63 - AIH-1-4
P. 63
Artificial Intelligence in Health A fuzzy system for heartbeat classification
A B
C D
E F
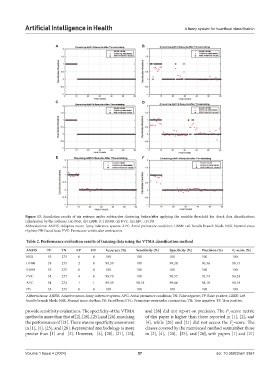
Figure 13. Simulation results of six systems under subtractive clustering before/after applying the variable threshold for check data classifications
(illustration by the authors). (A) NSR. (B) LBBB. (C) RBBB. (E) PVC. (E) APC. (F) PB
Abbreviations: ANFIS: Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system; APC: Atrial premature condition; LBBB: Left bundle branch block; NSR: Normal sinus
rhythm; PB: Paced beat; PVC: Premature ventricular contraction.
Table 2. Performance evaluation results of training data using the VTMA classification method
ANFIS TP TN FP FN Accuracy (%) Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) Precision (%) F -score (%)
1
NSR 55 275 0 0 100 100 100 100 100
LBBB 53 275 2 0 99.39 100 99.28 96.36 98.15
RBBB 55 275 0 0 100 100 100 100 100
PVC 51 275 4 0 98.79 100 98.57 92.73 96.23
APC 54 274 1 1 99.39 98.18 99.64 98.18 98.18
PB 55 275 0 0 100 100 100 100 100
Abbreviations: ANFIS: Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system; APC: Atrial premature condition; FN: False negative; FP: False positive; LBBB: Left
bundle branch block; NSR: Normal sinus rhythm; PB: Paced beat; PVC: Premature ventricular contraction; TN: True negative; TP: True positive.
provide sensitivity evaluations. The specificity of the VTMA and [26] did not report on precision. The F -score metric
1
method is more than that of [2], [20], [25], and [26], matching of this paper is higher than those reported in [1], [2], and
the performance of [21]. There was no specificity assessment [4], while [20] and [21] did not access the F -score. The
1
in [1], [4], [25], and [26]. Represented methodology is more classes covered by the mentioned method outnumber those
precise than [1] and [2]. However, [4], [20], [21], [25], in [2], [4], [20], [25], and [26], with papers [1] and [21]
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2024) 57 doi: 10.36922/aih.3367