Page 60 - AIH-1-4
P. 60
Artificial Intelligence in Health A fuzzy system for heartbeat classification
A B C
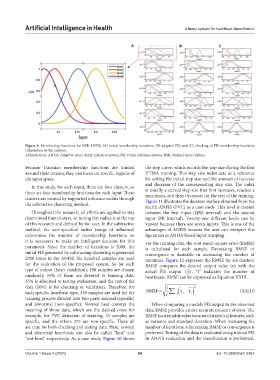
Figure 9. Membership functions for NSR ANFIS, (A) initial membership functions, (B) adapted FIS, and (C) checking of FIS membership functions
(illustration by the authors)
Abbreviations: ANFIS: Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system; FIS: Fuzzy inference system; NSR: Normal sinus rhythm.
Because Gaussian membership functions are limited the step curve, which records the step size during the first
around their centers, they can focus on specific regions of VTMA training. This step size index acts as a reference
the input space. for setting the initial step size and the amount of increase
and decrease of the corresponding step size. The index
In this study, for each input, there are four clusters, so
there are four membership functions for each input. These is usually a curved step size that first increases, reaches a
maximum, and then decreases for the rest of the training.
clusters are created by supported influence radius through Figure 11 illustrates the decision surface obtained from the
the subtractive clustering method.
fourth ANFIS (PVC) as a case study. This level is created
Throughout the research, all efforts are applied to stay between the first input (QRS interval) and the second
determined four clusters, so tuning this radius is at the top input (PR interval). Twenty-one different levels can be
of this research and defined by the user. In the subtractive viewed because there are seven inputs. This is one of the
method, the user-specified radius (range of influence) advantages of ANFIS because the user can interpret this
determines the number of membership functions, so figuration as ANFIS-based input mapping.
it is necessary to make an intelligent decision for this For the training data, the root-mean-square error (RMSE)
parameter. Since the number of iterations is 2000, the is calculated for each sample. Decreasing RMSE or
initial FIS generated by subtracting clustering is generated convergence is desirable in increasing the number of
2000 times in the ANFIS. Six hundred samples are used iterations. Figure 12 expresses the RMSE for six clusters.
for the evaluation of the proposed system. So for each RMSE compares the desired output value (y) with the
type of output (heart condition), 100 samples are chosen actual FIS output ( ˘)y . “t” indicates the number of
randomly, 55% of them are devoted to training data, heartbeats. RMSE can be expressed as Equation XXIII.
35% is allocated to testing evaluation, and the rest of the
data (10%) is for checking or validation. Therefore, for 1 t i ( i) 2
each specific heartbeat type, 330 samples are used for the RMSE = t ∑ i =1 y − y (XXIII)
training process divided into two parts: normal (specific)
and abnormal (non-specific). Normal beat conveys the When comparing a model’s FIS output to the observed
meaning of those data, which are the desired ones; for data, RMSE provides a more accurate measure of error. The
example, for PVC detection of training, 55 samples are RMSE is a desirable value because of statistical features, such
specific, and the others 275 are non-specific. These all as variance and standard deviation. When increasing the
are true for both checking and testing data. Here, normal number of iterations, a decreasing RMSE or convergence is
and abnormal heartbeats can also be called “beat” and preferred. Testing of the data is evaluated using trained FIS
“not-beat,” respectively. As a case study, Figure 10 shows in ANFIS evaluation and the classification is performed.
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2024) 54 doi: 10.36922/aih.3367