Page 62 - AIH-1-4
P. 62
Artificial Intelligence in Health A fuzzy system for heartbeat classification
A B
C D
E
F
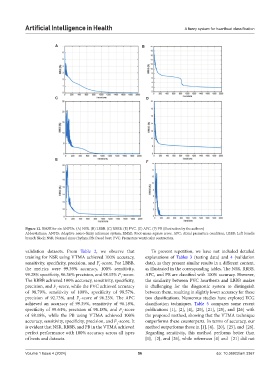
Figure 12. RMSE for six ANFISs. (A) NSR. (B) LBBB. (C) RBBB. (E) PVC. (E) APC. (F) PB (illustration by the authors)
Abbreviations: ANFIS: Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system; RMSE: Root-mean-square error; APC: Atrial premature condition; LBBB: Left bundle
branch block; NSR: Normal sinus rhythm; PB: Paced beat; PVC: Premature ventricular contraction.
validation datasets. From Table 2, we observe that To prevent repetition, we have not included detailed
training for NSR using VTMA achieved 100% accuracy, explanations of Tables 3 (testing data) and 4 (validation
sensitivity, specificity, precision, and F -score. For LBBB, data), as they present similar results in a different context,
1
the metrics were 99.39% accuracy, 100% sensitivity, as illustrated in the corresponding tables. The NSR, RBBB,
99.28% specificity, 96.36% precision, and 98.15% F -score. APC, and PB are classified with 100% accuracy. However,
1
The RBBB achieved 100% accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, the similarity between PVC heartbeats and LBBB makes
precision, and F -score, while the PVC achieved accuracy it challenging for the diagnostic system to distinguish
1
of 98.79%, sensitivity of 100%, specificity of 98.57%, between them, resulting in slightly lower accuracy for these
precision of 92.73%, and F -score of 96.23%. The APC two classifications. Numerous studies have explored ECG
1
achieved an accuracy of 99.39%, sensitivity of 98.18%, classification techniques. Table 5 compares some recent
specificity of 99.64%, precision of 98.18%, and F -score publications [1], [2], [4], [20], [21], [25], and [26] with
1
of 98.18%, while the PB using VTMA achieved 100% the proposed method, showing that the VTMA technique
accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, precision, and F -score. It outperforms these counterparts. In terms of accuracy, our
1
is evident that NSR, RBBB, and PB in the VTMA achieved method outperforms those in [1], [4], [20], [25], and [26].
perfect performance with 100% accuracy across all types Regarding sensitivity, this method performs better than
of beats and datasets. [1], [2], and [26], while references [4] and [21] did not
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2024) 56 doi: 10.36922/aih.3367