Page 83 - AIH-1-4
P. 83
Artificial Intelligence in Health Robotics and Vivaldi AI for ALS assessment
patients have the flexibility to request repetitions of questionnaire administration. This grid also
questions or take brief pauses using vocal commands. On documented patient reactions and behaviors.
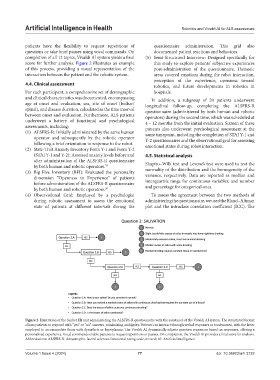
completion of all 12 topics, Vivaldi AI system yields a final (5) Semi-Structured Interview: Designed specifically for
score for further analysis. Figure 2 illustrates an example this study to explore patients’ subjective experiences
of this process, providing a visual representation of the post-administration of the questionnaire. Thematic
interaction between the patient and the robotic system. areas covered emotions during the robot interaction,
perception of the experience, openness toward
4.4. Clinical assessment robotics, and future developments in robotics in
For each participant, a comprehensive set of demographic hospitals.
and clinical characteristics was documented, encompassing In addition, a subgroup of 20 patients underwent
age at onset and evaluation, sex, site of onset (bulbar/ longitudinal follow-up, completing the ALSFRS-R
spinal), and disease duration, calculated as the time interval questionnaire (administered by both human and robotic
between onset and evaluation. Furthermore, ALS patients operators) during the second time, which was scheduled at
underwent a battery of functional and psychological 4 – 12 months from the initial evaluation. Sixteen of these
assessments, including: patients also underwent psychological assessment at the
(1) ALSFRS-R: Initially administered by the same human same timepoint, including the completion of STAI Y-1 and
operator and subsequently by the robotic operator Y-2 questionnaires and the observational grid for assessing
following a brief orientation in response to the robot.
(2) State-Trait Anxiety Inventory Form Y-1 and Form Y-2 emotional states during robot interaction.
(STAI Y-1 and Y-2): Assessed anxiety levels before and 4.5. Statistical analysis
after administration of the ALSFRS-R questionnaire Shapiro–Wilk test and Levene’s test were used to test the
by both human and robotic operators. 29
(3) Big Five Inventory (BFI): Evaluated the personality normality of the distribution and the homogeneity of the
dimension “Openness to Experience” of patients variance, respectively. Data are reported as median and
before administration of the ALSFRS-R questionnaire interquartile range for continuous variables, and number
by both human and robotic operators. 30 and percentage for categorical ones.
(4) Observational Grid: Employed by a psychologist To assess the agreement between the two methods of
during robotic assessment to assess the emotional administering the questionnaire, we used the Bland–Altman
state of patients at different intervals during the plot and the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC). The
Figure 2. Illustration of the Sanbot Elf unit administering the ALSFRS-R questionnaire with the assistance of the Vivaldi AI system. The structured format
allows patients to respond with “yes” or “no” answers, minimizing ambiguity. Patients can interact through verbal responses or touchscreen, with the latter
employed to accommodate those with dysarthria or hypophonia. The Vivaldi AI dynamically adjusts question sequences based on responses, offering a
personalized experience. Vocal commands enable patients to request repetitions or pauses. On completion, the Vivaldi AI provides a final score for analysis.
Abbreviations: ALSFRS-R: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis functional rating scale-revised; AI: Artificial intelligence.
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2024) 77 doi: 10.36922/aih.3732