Page 86 - AIH-1-4
P. 86
Artificial Intelligence in Health Robotics and Vivaldi AI for ALS assessment
A B
C D
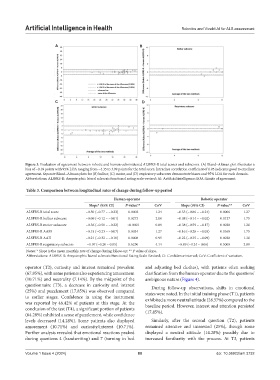
Figure 3. Evaluation of agreement between robotic and human-administered ALSFRS-R total scores and subscores. (A) Bland–Altman plot illustrates a
bias of −0.18 points with 95% LOA ranging from −4.35 to 3.99 points for the total score. Intraclass correlation coefficient of 0.95 indicates good to excellent
agreement. Separate Bland–Altman plots for (B) bulbar, (C) motor, and (D) respiratory subscores demonstrate biases and 95% LOA for each domain.
Abbreviations: ALSFRS-R: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis functional rating scale-revised; AI: Artificial intelligence; LOA: Limits of agreement.
Table 3. Comparison between longitudinal rates of change during follow‑up period
Human operator Robotic operator
Slope* (95% CI) P‑value** CoV Slope (95% CI) P‑value** CoV
ALSFRS-R total score −0.50 (−0.77 – −0.23) 0.0002 1.24 −0.55 (−0.86 – −0.24) 0.0006 1.27
ALSFRS-R bulbar subscore −0.06 (−0.12 – −0.01) 0.0273 2.00 −0.08 (−0.14 – −0.02) 0.0137 1.75
ALSFRS-R motor subscore −0.36 (−0.50 – −0.22) <0.0001 0.89 −0.38 (−0.59 – −0.17) 0.0020 1.26
ALSFRS-R AASS −0.15 (−0.23 – −0.07) 0.0034 1.27 −0.16 (−0.28 – −0.03) 0.0166 1.75
ALSFRS-R AAII −0.21 (−0.32 – −0.10) 0.0008 0.95 −0.22 (−0.35 – −0.09) 0.0028 1.36
ALSFRS-R respiratory subscore −0.07 (−0.20 – 0.05) 0.6250 4.14 −0.09 (−0.24 – 0.06) 0.5000 3.89
Notes: * Slope is the mean monthly rate of change during follow-up; ** P value of slope.
Abbreviations: ALSFRS-R: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Functional Rating Scale-Revised; CI: Confidence interval; CoV: Coefficient of variation.
operator (T2), curiosity and interest remained prevalent and adjusting bed clothes), with patients often seeking
(67.85%), with some patients also experiencing amusement clarification from the human operator due to the questions’
(10.71%) and neutrality (7.14%). By the midpoint of the ambiguous nature (Figure 4).
questionnaire (T3), a decrease in curiosity and interest During follow-up observations, shifts in emotional
(25%) and puzzlement (17.85%) was observed compared states were noted. In the initial training phase (T1), patients
to earlier stages. Confidence in using the instrument
was reported by 46.42% of patients at this stage. At the exhibited a more neutral attitude (28.57%) compared to the
baseline period. However, interest and attention persisted
conclusion of the test (T4), a significant portion of patients (17.85%).
(64.28%) exhibited a sense of puzzlement, while confidence
levels decreased (14.28%). Some patients also displayed Similarly, after the second question (T2), patients
amusement (10.71%) and curiosity/interest (10.71%). remained attentive and interested (25%), though some
Further analysis revealed that emotional reactions peaked displayed a neutral attitude (14.28%) possibly due to
during questions 4 (handwriting) and 7 (turning in bed increased familiarity with the process. At T3, patients
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2024) 80 doi: 10.36922/aih.3732