Page 108 - AIH-2-3
P. 108
Artificial Intelligence in Health Bone suppression utility for chest diagnosis
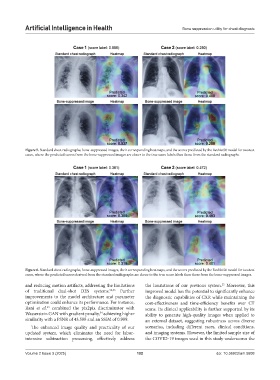
Figure 5. Standard chest radiographs, bone-suppressed images, their corresponding heatmaps, and the scores predicted by the ResNet50 model for two test
cases, where the predicted scores from the bone-suppressed images are closer to the true score labels than those from the standard radiographs.
Figure 6. Standard chest radiographs, bone-suppressed images, their corresponding heatmaps, and the scores predicted by the ResNet50 model for two test
cases, where the predicted scores derived from the standard radiographs are closer to the true score labels than those from the bone-suppressed images.
and reducing motion artifacts, addressing the limitations the limitations of our previous system. Moreover, this
22
of traditional dual-shot DES systems. 52,53 Further improved model has the potential to significantly enhance
improvements to the model architecture and parameter the diagnostic capabilities of CXR while maintaining the
optimization could enhance its performance. For instance, cost-effectiveness and time-efficiency benefits over CT
Rani et al. combined the pix2pix discriminator with scans. Its clinical applicability is further supported by its
23
Wasserstein GAN with gradient penalty, achieving higher ability to generate high-quality images when applied to
54
similarity with a PSNR of 43.588 and an SSIM of 0.989. an external dataset, suggesting robustness across diverse
The enhanced image quality and practicality of our scenarios, including different races, clinical conditions,
updated system, which eliminates the need for labor- and imaging systems. However, the limited sample size of
intensive subtraction processing, effectively address the COVID-19 images used in this study underscores the
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 102 doi: 10.36922/aih.5608