Page 78 - AIH-2-3
P. 78
Artificial Intelligence in Health CNN model for leukemia diagnosis
CNN model has a slight edge in correctly identifying both search and random search methods to identify the optimal
positive and negative cases, as seen from the higher values parameters for each model.
in TP and TN and lower values in FP and FN. Overall, CNN Expediting the training process in this paper is crucial
shows slightly better classification accuracy at this epoch, due to the large volume and high resolution of medical
as reflected in its confusion matrix. Key observations and images in the C-NMC dataset, which require substantial
conclusions from the graph are as follows: computational resources. By optimizing the training
• TP: Both CNN (solid line) and RNN (dashed line) process, we can significantly reduce the time and cost
show an increasing trend in TP across the epochs. CNN associated with developing and fine-tuning the DL models,
slightly outperforms RNN in identifying TP consistently. such as the proposed CNN.
• TN: The number of TN is also on the rise for both
algorithms over the epochs. Again, CNN achieves This acceleration is vital for iterative model
higher TN values compared to RNN. development, where multiple training cycles are needed
• FP: The FP remains relatively low and stable for both to refine model performance and tune hyperparameters.
algorithms, with minimal fluctuations. RNN has Moreover, efficient training ensures faster convergence,
slightly fewer FP compared to CNN throughout the leading to quicker deployment in clinical settings, where
epochs. timely and accurate leukemia diagnosis is critical. By
• FN: The FN is consistently low for both algorithms. expediting training, the model becomes more practical
CNN has a slightly lower FN rate compared to RNN. for real-world applications, allowing for rapid updates
with new data and scalable implementation across various
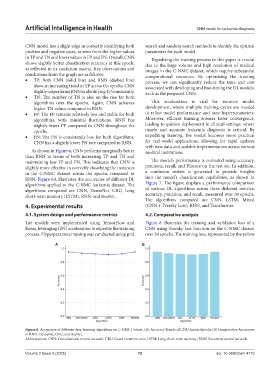
As shown in Figure 6, CNN performs marginally better medical institutions.
than RNN in terms of both increasing TP and TN and
maintaining low FP and FN. This indicates that CNN is The model’s performance is evaluated using accuracy,
slightly more effective in correctly classifying the instances precision, recall, and F1score on the test set. In addition,
in the C-NMC dataset across the epochs compared to a confusion matrix is generated to provide insights
RNN. Figure 6A illustrates the accuracies of different DL into the model’s classification capabilities, as shown in
algorithms applied to the C-NMC leukemia dataset. The Figure 7. The figure displays a performance comparison
algorithms compared are CNN, DenseNet, GRU, Long of various DL algorithms across three different metrics:
short-term memory (LSTM), RNN, and ResNet. accuracy, precision, and recall, measured over 30 epochs.
The algorithms compared are CNN, LSTM, Mixed
4. Experimental results (CNN + Tversky Loss), RNN, and Transformer.
4.1. System design and performance metrics 4.2. Comparative analysis
The models were implemented using TensorFlow and Figure 8 illustrates the training and validation loss of a
Keras, leveraging GPU acceleration to expedite the training CNN using Tversky loss function on the C-NMC dataset
process. Hyperparameter tuning was conducted using grid over 30 epochs. The training loss, represented by the yellow
A B
Figure 6. Accuracies of different deep learning algorithms on C-NMC Dataset. (A) Accuracy Trends of CNN Across Epochs (B) Comparative Accuracies
of RNN, DenseNet, GRU, and ResNet.
Abbreviations: CNN: Convolutional neural network; GRU: Gated recurrent unit; LSTM: Long short-term memory; RNN: Recurrent neural network.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 72 doi: 10.36922/aih.4710