Page 79 - AIH-2-3
P. 79
Artificial Intelligence in Health CNN model for leukemia diagnosis
A B C
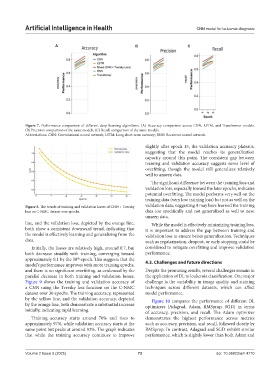
Figure 7. Performance comparison of different deep learning algorithms. (A) Accuracy comparison across CNN, LSTM, and Transformer models.
(B) Precision comparison of the same models. (C) Recall comparison of the same models.
Abbreviations: CNN: Convolutional neural network; LSTM: Long short-term memory; RNN: Recurrent neural network.
slightly after epoch 15, the validation accuracy plateaus,
suggesting that the model reaches its generalization
capacity around this point. The consistent gap between
training and validation accuracy suggests some level of
overfitting, though the model still generalizes relatively
well to unseen data.
The significant difference between the training loss and
validation loss, especially toward the later epochs, indicates
potential overfitting. The model performs very well on the
training data (very low training loss) but not as well on the
Figure 8. The trends of training and validation losses of CNN + Tversky validation data, suggesting it may have learned the training
loss on C-NMC dataset over epochs. data too specifically and not generalized as well to new,
unseen data.
line, and the validation loss, depicted by the orange line, While the model is effectively minimizing training loss,
both show a consistent downward trend, indicating that it is important to address the gap between training and
the model is effectively learning and generalizing from the validation loss to ensure better generalization. Techniques
data. such as regularization, dropout, or early stopping could be
Initially, the losses are relatively high, around 0.7, but considered to mitigate overfitting and improve validation
both decrease steadily with training, converging toward performance.
approximately 0.1 by the 30 epoch. This suggests that the
th
model’s performance improves with more training epochs, 4.3. Challenges and future directions
and there is no significant overfitting, as evidenced by the Despite the promising results, several challenges remain in
parallel decrease in both training and validation losses. the application of DL to leukemia classification. One major
Figure 9 shows the training and validation accuracy of challenge is the variability in image quality and staining
a CNN using the Tversky loss function on the C-NMC techniques across different datasets, which can affect
dataset over 30 epochs. The training accuracy, represented model performance.
by the yellow line, and the validation accuracy, depicted Figure 10 compares the performance of different DL
by the orange line, both demonstrate a substantial increase optimizers (Adagrad, Adam, RMSprop, SGD) in terms
initially, indicating rapid learning. of accuracy, precision, and recall. The Adam optimizer
Training accuracy starts around 70% and rises to demonstrates the highest performance across metrics
approximately 97%, while validation accuracy starts at the such as accuracy, precision, and recall, followed closely by
same point but peaks at around 92%. The graph indicates RMSprop. In contrast, Adagrad and SGD exhibit similar
that while the training accuracy continues to improve performance, which is slightly lower than both Adam and
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 73 doi: 10.36922/aih.4710