Page 207 - AJWEP-22-4
P. 207
Bombax ceiba-based carbons for dye removal
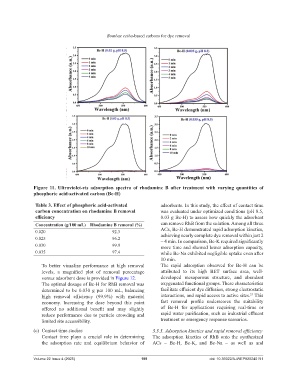
Figure 11. Ultraviolet-vis adsorption spectra of rhodamine B after treatment with varying quantities of
phosphoric acid-activated carbon (Bc-H)
Table 3. Effect of phosphoric acid-activated adsorbents. In this study, the effect of contact time
carbon concentration on rhodamine B removal was evaluated under optimized conditions (pH 8.5,
efficiency 0.03 g Bc-H) to assess how quickly the adsorbent
Concentration (g/100 mL) Rhodamine B removal (%) can remove RhB from the solution. Among all three
0.020 92.3 ACs, Bc-H demonstrated rapid adsorption kinetics,
0.025 96.2 achieving nearly complete dye removal within just 2
– 4 min. In comparison, Bc-K required significantly
0.030 99.9 more time and showed lower adsorption capacity,
0.035 97.4 while Bc-Na exhibited negligible uptake even after
10 min.
To better visualize performance at high removal The rapid adsorption observed for Bc-H can be
levels, a magnified plot of removal percentage attributed to its high BET surface area, well-
versus adsorbent dose is provided in Figure 12. developed mesoporous structure, and abundant
The optimal dosage of Bc-H for RhB removal was oxygenated functional groups. These characteristics
determined to be 0.030 g per 100 mL, balancing facilitate efficient dye diffusion, strong electrostatic
21
high removal efficiency (99.9%) with material interactions, and rapid access to active sites. This
economy. Increasing the dose beyond this point fast removal profile underscores the suitability
offered no additional benefit and may slightly of Bc-H for applications requiring real-time or
reduce performance due to particle crowding and rapid water purification, such as industrial effluent
limited site accessibility. treatment or emergency response scenarios.
(c) Contact time studies 3.3.3. Adsorption kinetics and rapid removal efficiency
Contact time plays a crucial role in determining The adsorption kinetics of RhB onto the synthesized
the adsorption rate and equilibrium behavior of ACs – Bc-H, Bc-K, and Bc-Na – as well as and
Volume 22 Issue 4 (2025) 199 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025240191