Page 203 - AJWEP-22-4
P. 203
Bombax ceiba-based carbons for dye removal
Bc-Na exhibited sharper C=C bands and fewer polar
groups, consistent with higher thermal degradation
and deoxygenation during alkaline activation. These
14
surface functionalities are crucial for dye adsorption. In
particular, hydroxyl, carbonyl, phosphate, and aromatic
groups are expected to facilitate electrostatic attraction,
hydrogen bonding, and π–π stacking interactions with
Rh B molecules, enhancing adsorption capacity and
rate.
3.2.6. Physicochemical properties in the adsorption of
cationic dye
The adsorption performance of the AC samples toward
RhB is strongly influenced by their physicochemical
characteristics, as revealed by XRD, Raman
spectroscopy, SEM, BET, and FTIR analyses.
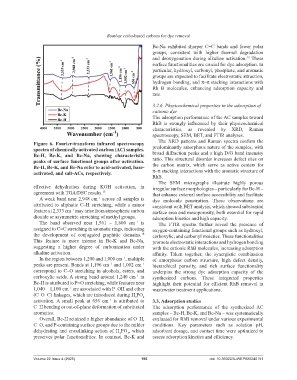
Figure 6. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy The XRD patterns and Raman spectra confirm the
spectra of chemically activated carbon (AC) samples. predominantly amorphous nature of the samples, with
Bc-H, Bc-K, and Bc-Na, showing characteristic broad diffraction peaks and a high D/G band intensity
peaks of surface functional groups after activation. ratio. This structural disorder increases defect sites on
Bc-H, Bc-K, and Bc-Na refer to acid-activated, base- the carbon matrix, which serve as active centers for
activated, and salt-ACs, respectively. π–π stacking interactions with the aromatic structure of
RhB.
The SEM micrographs illustrate highly porous
effective dehydration during KOH activation, in irregular surface morphologies – particularly for Bc-H –
agreement with TGA/DSC results. 13 that enhance external surface accessibility and facilitate
A weak band near 2,948 cm across all samples is dye molecule penetration. These observations are
−1
attributed to aliphatic C–H stretching, while a minor consistent with BET analysis, which showed substantial
feature at 2,333 cm may arise from atmospheric carbon surface area and mesoporosity, both essential for rapid
−1
dioxide or asymmetric stretching of methyl groups. adsorption kinetics and high capacity.
The band observed near 1,561 – 1,600 cm is The FTIR spectra further reveal the presence of
−1
assigned to C=C stretching in aromatic rings, indicating oxygen-containing functional groups such as hydroxyl,
the development of conjugated graphitic domains. carboxylic, and carbonyl moieties. These functionalities
18
This feature is more intense in Bc-K and Bc-Na, promote electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonding
suggesting a higher degree of carbonization under with the cationic RhB molecules, increasing adsorption
alkaline activation. affinity. Taken together, the synergistic combination
In the region between 1,200 and 1,000 cm , multiple of amorphous carbon structure, high defect density,
−1
peaks are present. Bands at 1,196 cm and 1,002 cm hierarchical porosity, and rich surface functionality
−1
−1
correspond to C–O stretching in alcohols, esters, and underpins the strong dye adsorption capacity of the
carboxylic acids. A strong band around 1,240 cm in synthesized carbons. These integrated properties
−1
Bc-H is attributed to P=O stretching, while features near highlight their potential for efficient RhB removal in
1,040 – 1,100 cm are associated with P–OH and ether wastewater treatment applications.
−1
(C–O–C) linkages, which are introduced during H PO
3
4
activation. A small peak at 656 cm is attributed to 3.3. Adsorption studies
−1
C–H bending or out-of-plane deformation of substituted The adsorption performance of the synthesized AC
aromatics. samples – Bc-H, Bc-K, and Bc-Na – was systematically
Overall, Bc-H retained a higher abundance of O–H, evaluated for RhB removal under various experimental
C–O, and P-containing surface groups due to the milder conditions. Key parameters such as solution pH,
dehydrating and crosslinking action of H PO , which adsorbent dosage, and contact time were optimized to
3
4
preserves polar functionalities. In contrast, Bc-K and assess adsorption kinetics and efficiency.
Volume 22 Issue 4 (2025) 195 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025240191