Page 205 - AJWEP-22-4
P. 205
Bombax ceiba-based carbons for dye removal
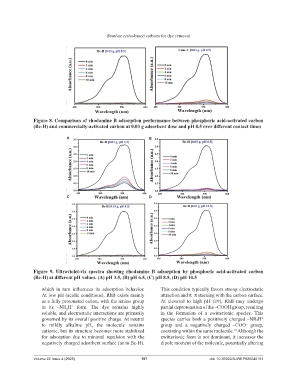
Figure 8. Comparison of rhodamine B adsorption performance between phosphoric acid-activated carbon
(Bc-H) and commercially-activated carbon at 0.03 g adsorbent dose and pH 8.5 over different contact times
A B
C D
Figure 9. Ultraviolet-vis spectra showing rhodamine B adsorption by phosphoric acid-activated carbon
(Bc-H) at different pH values. (A) pH 3.5, (B) pH 6.5, (C) pH 8.5, (D) pH 10.5
which in turn influences its adsorption behavior. This condition typically favors strong electrostatic
At low pH (acidic conditions), RhB exists mainly attraction and π–π stacking with the carbon surface.
as a fully protonated cation, with the amino group At elevated to high pH (≥9), RhB may undergo
in its –NR H form. The dye remains highly partial deprotonation of the –COOH group, resulting
+
2
soluble, and electrostatic interactions are primarily in the formation of a zwitterionic species. This
governed by its overall positive charge. At neutral species carries both a positively charged –NR₂H⁺
to mildly alkaline pH, the molecule remains group and a negatively charged –COO⁻ group,
cationic, but its structure becomes more stabilized coexisting within the same molecule. Although the
15
for adsorption due to minimal repulsion with the zwitterionic form is not dominant, it increases the
negatively charged adsorbent surface (as in Bc-H). dipole moment of the molecule, potentially altering
Volume 22 Issue 4 (2025) 197 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025240191