Page 78 - AJWEP-22-4
P. 78
Tanko, et al.
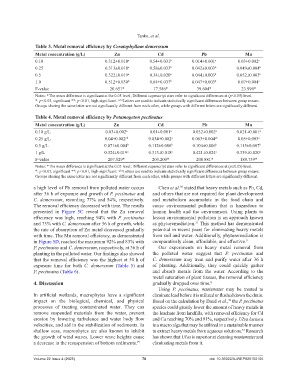
Table 3. Metal removal efficiency by Ceratophyllum demerssum
Metal concentration (g/L) Zn Cd Pb Mn
0.10 0.312±0.018 a 0.54±0.031 b 0.014±0.001 a 0.03±0.002 a
0.25 0.313±0.018 a 0.58±0.033 b 0.042±0.003 b 0.049±0.004 b
0.5 0.322±0.019 a 0.34±0.020 a 0.044±0.003 b 0.052±0.003 b
1.0 0.512±0.030 b 0.64±0.037 b 0.047±0.003 b 0.07±0.004 c
F-value 20.651* 17.586* 39.604* 23.999*
Notes: *The mean difference is significant at the 0.05 level; Different superscript stars refer to significant differences at (p≤0.05) level.
*: p<0.05, significant **: p<0.01, high-significant. a,b,c Letters are used to indicate statistically significant differences between group means.
Groups sharing the same letter are not significantly different from each other, while groups with different letters are significantly different.
Table 4. Metal removal efficiency by Potamogeton pectinatus
Metal concentration (g/L) Zn Cd Pb Mn
0.10 g/L 0.03±0.002 a 0.01±0.001 a 0.032±0.002 a 0.021±0.001 a
0.25 g/L 0.04±0.002 ab 0.034±0.002 a 0.063±0.004 ab 0.05±0.003 a
0.5 g/L 0.071±0.004 b 0.112±0.006 b 0.104±0.006 b 0.115±0.007 b
1 g/L 0.324±0.019 c 0.313±0.018 c 0.421±0.024 c 0.339±0.020 c
F-value 207.829* 203.200* 200.881* 189.739*
Notes: *The mean difference is significant at the 0.05 level; Different superscript stars refer to significant differences at (p≤0.05) level.
*: p<0.05, significant **: p<0.01, high-significant. a,b,c Letters are used to indicate statistically significant differences between group means.
Groups sharing the same letter are not significantly different from each other, while groups with different letters are significantly different.
a high level of Pb removal from polluted water occurs Chen et al. stated that heavy metals such as Pb, Cd,
30
after 36 h of exposure and growth of P. pectinatus and and others that are not required for plant development
C. demerssum, recording 77% and 54%, respectively. and metabolism accumulate in the food chain and
The removal efficiency decreased with time. The results cause environmental pollution that is hazardous to
presented in Figure 5C reveal that the Zn removal human health and the environment. Using plants to
efficiency was high, reaching 94% with P. pectinatus lessen environmental pollution is an approach known
and 73% with C. demerssum after 36 h of growth, while as phytoremediation. This method has demonstrated
31
the rate of absorption of Zn metal decreased gradually potential in recent years for eliminating heavy metals
with time. The Mn removal efficiency, as demonstrated from soil and water. Additionally, phytoremediation is
in Figure 5D, reached the maximum 92% and 83% with comparatively clean, affordable, and effective. 9
P. pectinatus and C. demerssum, respectively, at 36 h of Our experiments on heavy metal removal from
planting in the polluted water. Our findings also showed the polluted water suggest that P. pectinatus and
that the removal efficiency was the highest at 30 h of C. demerssum may treat and purify water after 36 h
exposure time for both C. demerssum (Table 5) and of planting. Additionally, they could quickly gather
P. pectinatus (Table 6). and absorb metals from the water. According to the
metal saturation of plant tissues, the removal efficiency
4. Discussion gradually dropped over time. 8
Using P. pectinatus, wastewater may be treated to
In artificial wetlands, macrophytes have a significant eliminate lead before it is utilized or flushed down the drain.
impact on the biological, chemical, and physical Based on the calculation by Daud et al., the P. pectinatus
32
processes of treating contaminated water. They can species could greatly lower the amount of heavy metals in
remove suspended materials from the water, prevent the leachate from landfills, with removal efficiency for Cd
erosion by lowering turbulence and water body flow and Cu reaching 70% and 91%, respectively. Ulva lactuca
velocities, and aid in the stabilization of sediments. In is a macro alga that may be utilized in a sustainable manner
shallow seas, macrophytes are also known to inhibit to extract heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Research
33
the growth of wind waves. Lower wave heights cause has shown that Ulva is superior at cleaning wastewater and
a decrease in the resuspension of bottom sediments. 29 eliminating metals from it.
Volume 22 Issue 4 (2025) 70 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025150105