Page 130 - AJWEP-22-6
P. 130
Kuppusamy and Dhanasamy
A B C
D E F
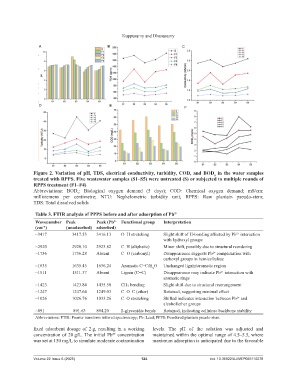
Figure 2. Variation of pH, TDS, electrical conductivity, turbidity, COD, and BOD in the water samples
5
treated with RPPS. Five wastewater samples (S1–S5) were untreated (S) or subjected to multiple rounds of
RPPS treatment (F1–F4)
Abbreviations: BOD : Biological oxygen demand (5 days); COD: Chemical oxygen demand; mS/cm:
5
millisiemens per centimetre; NTU: Nephelometric turbidity unit; RPPS: Raw plantain pseudo-stem;
TDS: Total dissolved solids
Table 3. FTIR analysis of PPPS before and after adsorption of Pb 2+
Wavenumber Peak Peak (Pb²⁺ Functional group Interpretation
(cm⁻¹) (unadsorbed) adsorbed)
~3417 3417.53 3416.13 O–H stretching Slight shift of H-bonding affected by Pb²⁺ interaction
with hydroxyl groups
~2920 2920.10 2923.82 C–H (aliphatic) Minor shift, possibly due to structural reordering
~1736 1736.28 Absent C=O (carbonyl) Disappearance suggests Pb²⁺ complexation with
carboxyl groups in hemicellulose
~1635 1635.45 1636.24 Aromatic C=C/H O Unchanged lignin/aromatic region
2
~1511 1511.37 Absent Lignin (C=C) Disappearance may indicate Pb²⁺ interaction with
aromatic rings
~1423 1423.84 1435.50 CH₂ bending Slight shift due to structural rearrangement
~1247 1247.64 1249.03 C–O–C (ether) Retained, suggesting minimal effect
~1026 1026.76 1033.26 C–O stretching Shifted indicates interaction between Pb²⁺ and
alcohol/ether groups
~891 891.63 894.20 β-glycosidic bonds Retained, indicating cellulose backbone stability
Abbreviations: FTIR: Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy; Pb: Lead; PPPS: Powdered plantain pseudo-stem.
fixed adsorbent dosage of 2 g, resulting in a working levels. The pH of the solution was adjusted and
concentration of 20 g/L. The initial Pb²⁺ concentration maintained within the optimal range of 4.5–5.5, where
was set at 150 mg/L to simulate moderate contamination maximum adsorption is anticipated due to the favorable
Volume 22 Issue 6 (2025) 124 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025110078