Page 131 - AJWEP-22-6
P. 131
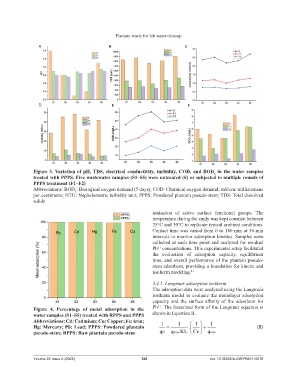
Plantain waste for lab water cleanup
A B C
D E F
Figure 3. Variation of pH, TDS, electrical conductivity, turbidity, COD, and BOD in the water samples
5
treated with PPPS. Five wastewater samples (S1–S5) were untreated (S) or subjected to multiple rounds of
PPPS treatment (F1–F2)
Abbreviations: BOD : Biological oxygen demand (5 days); COD: Chemical oxygen demand; mS/cm: millisiemens
5
per centimetre; NTU: Nephelometric turbidity unit; PPPS: Powdered plantain pseudo-stem; TDS: Total dissolved
solids
ionization of active surface functional groups. The
temperature during the study was kept constant between
25°C and 30°C to replicate typical ambient conditions.
Contact time was varied from 0 to 180 min at 30-min
intervals to monitor adsorption kinetics. Samples were
collected at each time point and analyzed for residual
Pb²⁺ concentrations. This experimental setup facilitated
the evaluation of adsorption capacity, equilibrium
time, and overall performance of the plantain pseudo-
stem adsorbent, providing a foundation for kinetic and
isotherm modeling. 41
3.4.1. Langmuir adsorption isotherm
The adsorption data were analyzed using the Langmuir
isotherm model to evaluate the monolayer adsorption
capacity and the surface affinity of the adsorbent for
Figure 4. Percentage of metal adsorption in the Pb²⁺. The linearized form of the Langmuir equation is
water samples (S1–S5) treated with RPPS and PPPS shown in Equation II.
Abbreviations: Cd: Cadmium; Cu: Copper; Fe: Iron;
Hg: Mercury; Pb: Lead; PPPS: Powdered plantain 1 1 . 1 1 (II)
pseudo-stem; RPPS: Raw plantain pseudo-stem qe qmax. KL Ce qmax
Volume 22 Issue 6 (2025) 125 doi: 10.36922/AJWEP025110078