Page 105 - AJWEP-v22i2
P. 105
Assessing drought impacts for adaptive response
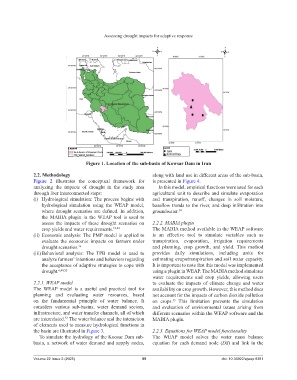
Figure 1. Location of the sub-basin of Kowsar Dam in Iran
2.2. Methodology along with land use in different areas of the sub-basin,
Figure 2 illustrates the conceptual framework for is presented in Figure 4.
analyzing the impacts of drought in the study area In this model, empirical functions were used for each
through four interconnected steps: agricultural unit to describe and simulate evaporation
(i) Hydrological simulation: The process begins with and transpiration, runoff, changes in soil moisture,
hydrological simulation using the WEAP model, baseflow trends to the river, and deep infiltration into
where drought scenarios are defined. In addition, groundwater. 54
the MABIA plugin in the WEAP tool is used to
assess the impacts of these drought scenarios on 2.2.2. MABIA plugin
crop yields and water requirements. 12,24 The MABIA method available in the WEAP software
(ii) Economic analysis: The PMP model is applied to is an effective tool to simulate variables such as
evaluate the economic impacts on farmers under transpiration, evaporation, irrigation requirements
drought scenarios. 36 and planning, crop growth, and yield. This method
(iii) Behavioral analysis: The TPB model is used to provides daily simulations, including units for
analyze farmers’ intentions and behaviors regarding estimating evapotranspiration and soil water capacity.
the acceptance of adaptive strategies to cope with It is important to note that this model was implemented
drought. 6,44,52 using a plugin in WEAP. The MABIA method simulates
water requirements and crop yields, allowing users
2.2.1. WEAP model to evaluate the impacts of climate change and water
The WEAP model is a useful and practical tool for availability on crop growth. However, this method does
planning and evaluating water resources, based not account for the impacts of carbon dioxide pollution
on the fundamental principle of water balance. It on crops. This limitation prevents the simulation
35
considers various sub-basins, water demand sectors, and evaluation of environmental issues arising from
infrastructure, and water transfer channels, all of which different scenarios within the WEAP software and the
are interrelated. The water balance and the interaction MABIA plugin.
53
of elements used to measure hydrological functions in
the basin are illustrated in Figure 3. 2.2.3. Equations for WEAP model functionality
To simulate the hydrology of the Koosar Dam sub- The WEAP model solves the water mass balance
basin, a network of water demand and supply nodes, equation for each demand node (DS) and link in the
Volume 22 Issue 2 (2025) 99 doi: 10.36922/ajwep.8381