Page 82 - ARNM-2-4
P. 82
Advances in Radiotherapy
& Nuclear Medicine Dose-volume histogram and gamma analysis
of localized prostate cancer. Today, it is known that the percentage of approved points, the treatment plan is
3
enhancing the local control of a disease requires a dose approved for use in the patient. The acceptable gamma
increase for treatment planning target volume (PTV). passing rates range from 90% to 95%.
However, this often poses a challenge when considering the Even so, not all the parameters for this assessment are
dose tolerances of adjacent normal tissues. Separately, the fully established. To overcome these challenges, guidelines
European Guidelines recommended the use of intensity- were developed to provide better guidance on the proper
modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) as the standard selection and use of the dosimetry tools available for IMRT
treatment for prostate cancer. 4,5 QA, including algorithms, software, and devices. One of
8
Planning with the IMRT technique allows the delivery the problems has been the effectiveness of using the gamma
of the dose to the PTV with a high degree of conformation index to evaluate the clinical relevance of delivering a dose
while satisfactorily restricting the dose limit in the organs to the patient, 9-11 because the gamma passing rates in the
at risk. The dose increase is achieved through subfields patient-specific quality assurance phantom geometry do
with different sizes and intensities, which compose a single not reflect the position and/or the amount of dose variation
modulated field, and generally, five to nine treatment in the patient’s body. Consequently, the divergences in the
fields are employed. The IMRT technique is characterized planned and measured patient’s dose-volume histogram
by generating very heterogeneous dose distributions and (DVH) cannot be computed.
promoting regions of high dose gradient very close to that To contribute to the understanding of the relationship
of critical organs. between the gamma index result and its clinical
Due to this high degree of complexity, strict quality significance, we propose a simulated study to find a
assurance is necessary to verify both the accuracy of the relationship between changes in dose values in the DVH of
treatment planning system (TPS) as well as the ability the evaluated structures and percentages of gamma index
to execute the radiation fields that will be configured approval and evaluate whether such changes are acceptable
in the linear accelerator (LINAC) during the treatment according to the dose constraints of the protocol used.
application. In addition, it is recommended by several
institutions and protocols, such as the American 2. Materials and methods
Association of Physicists in Medicine Task Group No. 218 This study utilized a simulated treatment plan for prostate
(AAPM TG218), that before beginning any treatment with cancer using the solid water phantom with the target
the IMRT technique, the patient-specific quality assurance volumes of treatment, bladder, and rectum already
should be performed to identify possible discrepancies delimited by the TG-119 protocol of AAPM. 12
between the calculated dose and the dose that will be
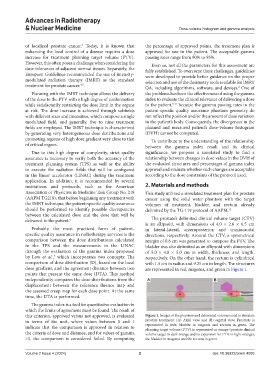
delivered to the patient. 6 The prostate’s delimited clinical volume target (CTV)
is an ellipsoid, with dimensions of 4.0 × 2.6 × 6.5 cm
Probably, the most practiced form of patient- in lateral-lateral, anteroposterior, and craniocaudal
specific quality assurance in radiotherapy services is the directions, respectively. Around the CTV, a symmetrical
comparison between the dose distributions calculated margin of 0.6 cm was generated to compose the PTV. The
in the TPS and the measurements in the LINAC bladder was also delimited as an ellipsoid with dimensions
through the evaluation of the gamma index proposed of 5.0 × 4.0 × 5.0 cm in width, thickness, and length,
by Low et al., which incorporates two concepts: The respectively. On the other hand, the rectum is cylindrical
7
comparison of dose distribution (D), based on the local with 1.5 cm in radius and 9.25 cm in length. The structures
dose gradient, and the agreement distance between two are represented in red, magenta, and green in Figure 1.
points that present the same dose (DTA). This method
independently compares the dose distributions from the A B
displacement between the reference fluence map and
the assessed creep map for each dose point. At the same
time, the DTA is performed.
The gamma index is a tool for quantitative evaluation in
which the limits of agreement must be found. The result of
this criterion, approved versus not approved, is evaluated Figure 1. Images of the phantom and delineated volumes used to simulate
in terms of the unit, where values between 0 and 1 prostate treatment: (A) Axial view and (B) sagittal view. Prostrate is
indicate that the comparison is approved in relation to represented in rede, bladder in magenta and rectum in green. The
planning target volume (PTV) is represented in orange (prostate clinical
the criteria of dose and distance, and for values of gamma volume target in dark orange and its expansion for PTV in light orange),
>1, the comparison is considered failed. By computing the bladder in magenta and the rectum in green.
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2024) 2 doi: 10.36922/arnm.4005