Page 115 - EER-2-1
P. 115
Explora: Environment
and Resource Carbon neutrality and low-carbon behavior in space tourism
α values post-item deletion remained below the latent explaining at least 50% cumulative variance. Separate
variable’s coefficients, further affirming the soundness of factor analyses were performed on six scales, revealing
the questionnaire (Table 4). convergence under six factors: Novelty cognition (NC),
disruption cognition (DC), criticality cognition (CC),
4.5. Validity analysis LCM, LCA, and low-carbon behavior intention (LCB) for
The validity test was conducted through factor analysis, space tourism. These factors accounted for approximately
and principal component analysis with varimax rotation 68% of the variation, with Eigenvalues greater than 1 for
was employed independently for each construct. Before all (Table 5).
this, “Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity” (BTS) was used to assess Confirmatory factor analysis was used as a
the presence of correlations, and the “Kaiser’s Measure of confirmatory test to assess the measurement tool, testing
Sampling Adequacy” (KMO) test was conducted to ensure how well-measured variables represent a smaller number
adequate sampling. Results indicated a KMO value above of constructs.
0.50 and a BTS value being significantly different from 0, The data analysis revealed that all 24 questions on
which are the prerequisites for performing factor analysis each variable scale had factor loadings exceeding 0.6,
(Hair et al., 2006). Extraction was based on Eigenvalue with significance at 0.001. All six constructs’ combination
criteria, retaining factors with Eigenvalues above one and reliability surpassed the 0.6 criterion, indicating
internal consistency. Furthermore, the Squared multiple
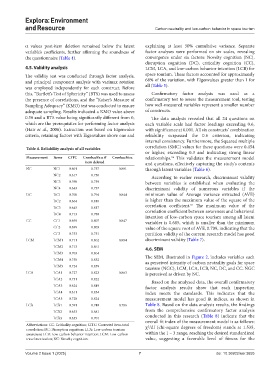
Table 4. Reliability analysis of all variables correlation (SMC) values for these questions were 0.454
or higher, exceeding 0.3 and indicating strong linear
Measurement Items CITC Cronbach’s α if Cronbach’s α relationships. This validates the measurement model
56
item deleted and questions, effectively capturing the study’s contents
NC NC1 0.601 0.757 0.801 through latent variables (Table 6).
NC2 0.617 0.750 According to earlier research, discriminant validity
NC3 0.598 0.759 between variables is established when evaluating the
NC4 0.643 0.737 discriminant validity of numerous variables if the
DC DC1 0.700 0.794 0.844 minimum value of Average variance extracted (AVE)
DC2 0.664 0.810 is higher than the maximum value of the square of the
57
DC3 0.645 0.817 correlation coefficient. The maximum value of the
correlation coefficient between awareness and behavioral
DC4 0.713 0.788
intention of low-carbon space tourism among all latent
CC CC1 0.695 0.807 0.847
variables is 0.685, which is smaller than the minimum
CC2 0.699 0.803 value of the square root of AVE, 0.709, indicating that the
CC3 0.753 0.751 partition validity of the current research model has good
LCM LCM1 0.711 0.862 0.884 discriminant validity (Table 7).
LCM2 0.713 0.861
4.6. SEM
LCM3 0.703 0.864
LCM4 0.758 0.852 The SEM, illustrated in Figure 2, includes variables such
as perceived intensity of carbon neutrality goals for space
LCM5 0.724 0.859 tourism (NGC), LCM, LCA, LCB, NC, DC, and CC. NGC
LCA LCA1 0.727 0.823 0.863 is perceived as driven by NC.
LCA2 0.731 0.822 Based on the analyzed data, the overall confirmatory
LCA3 0.624 0.849 factor analysis results show that each inspection
LCA4 0.611 0.854 index meets the standards. This indicates that the
LCA5 0.728 0.824 measurement model has good fit indices, as shown in
LCB LCB1 0.591 0.748 0.786 Table 8. Based on the data analysis results, the findings
LCB2 0.653 0.681 from the comprehensive confirmatory factor analysis
LCB3 0.635 0.701 conducted in this research (Table 8) indicate that the
Abbreviations: CC: Criticality cognition; CITC: Corrected item-total overall fit index of the measurement model is as follows:
χ /df (chi-square degrees of freedom) stands at 1.535,
2
correlation; DC: Disruption cognition; LCA: Low-carbon tourism
awareness; LCB: Low-carbon behavior intention; LCM: Low-carbon within the 1 – 3 range, reaching the desired standardized
travel motivation; NC: Novelty cognition. value, suggesting a favorable level of fitness for the
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2025) 7 doi: 10.36922/eer.3655