Page 100 - EER-2-3
P. 100
Explora: Environment
and Resource Comparative analysis of THMs and THAAs in water distribution media
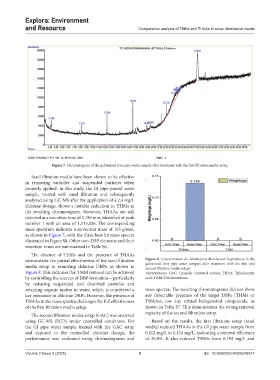
Figure 7. Chromatogram of the galvanized iron pipe water sample after treatment with the first filtration media setup
Sand filtration media have been shown to be effective
in removing turbidity and suspended particles when
properly applied. In this study, the GI pipe-passed water
sample, treated with sand filtration and subsequently
analyzed using GC-MS after the application of a 2.4 mg/L
chlorine dosage, shows a notable reduction in THMs in
the resulting chromatogram. However, THAAs are still
detected at a retention time of 3.196 min, identified at peak
number 1 with an area of 1,115,036. The corresponding
mass spectrum indicates a molecular mass of 165 g/mol,
as shown in Figure 7, with the three best-hit mass spectra
illustrated in Figure S8. Other non-DBP elements and their
retention times are summarized in Table S6.
The absence of THMs and the presence of THAAs
demonstrate the partial effectiveness of the sand filtration Figure 8. Concentration of chlorination disinfection byproducts in the
media setup in removing chlorine DBPs, as shown in galvanized iron pipe water samples after treatment with the first and
second filtration media setups
Figure 8. This indicates that THM removal can be achieved Abbreviations: GAC: Granular activated carbon; THAA: Trihaloacetic
by controlling the sources of DBP formation—particularly acid; THM: Trihalomethane.
by reducing suspended and dissolved particles and
retaining organic matter in water, which is considered a mass spectra. The resulting chromatograms did not show
key precursor to chlorine DBPs. However, the presence of any detectable presence of the target DBPs (THMs or
THAAs in the mass spectra challenges the full effectiveness THAAs), nor any related halogenated compounds, as
of the first filtration media setup. shown in Table S7. This demonstrates the strong removal
The second filtration media setup (GAC) was analyzed capacity of the second filtration setup.
using GC-MS (ECD) under controlled conditions. For Based on the results, the first filtration setup (sand
the GI pipe water sample treated with the GAC setup media) reduced THAAs in the GI pipe water sample from
and exposed to the controlled chlorine dosage, the 0.212 mg/L to 0.134 mg/L, indicating a removal efficiency
performance was evaluated using chromatograms and of 36.8%. It also reduced THMs from 0.193 mg/L and
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 9 doi: 10.36922/EER025240047