Page 96 - EER-2-3
P. 96
Explora: Environment
and Resource Comparative analysis of THMs and THAAs in water distribution media
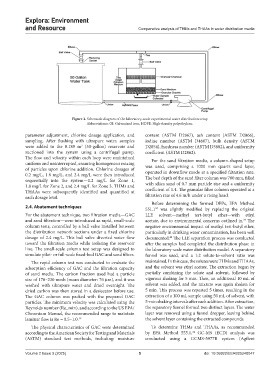
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of the laboratory-scale experimental water distribution setup
Abbreviations: GI: Galvanized iron; HDPE: High-density polyethylene.
parameter adjustment, chlorine dosage application, and content (ASTM D2867), ash content (ASTM D2866),
sampling. After flushing with ultrapure water, samples iodine number (ASTM D4607), bulk density (ASTM
3
were added to the 0.189 m (50-gallon) reservoir and D2854), hardness number (ASTM D3802), and uniformity
suctioned into the system using a centrifugal pump. coefficient (ASTM D2862).
The flow and velocity within each loop were maintained For the sand filtration media, a column-shaped setup
uniform and uninterrupted, ensuring homogenous mixing was used, comprising a 1000 mm quartz sand layer,
of particles upon chlorine addition. Chlorine dosages of operated in downflow mode at a specified filtration rate.
0.2 mg/L, 1.8 mg/L, and 2.4 mg/L were then introduced The bed depth of the sand filter column was 700 mm, filled
sequentially into the system—0.2 mg/L for Zone 1,
1.8 mg/L for Zone 2, and 2.4 mg/L for Zone 3. THMs and with silica sand of 0.7 mm particle size and a uniformity
THAAs were subsequently identified and quantified at coefficient of 1.4. The granular filter column operated at a
each dosage level. filtration rate of 4.6 m/h under a rising head.
Before determining the formed DBPs, EPA Method
2.4. Abatement techniques 551.1 was slightly modified by replacing the original
34
For the abatement technique, two filtration media—GAC LLE solvent—methyl tert-butyl ether—with ethyl
and sand filtration—were introduced as rapid, small-scale acetate, due to environmental concerns outlined in. The
34
column tests, controlled by a ball valve installed between negative environmental impact of methyl tert-butyl ether,
the distribution network sections under a fixed chlorine particularly in drinking water contamination, has been well
dosage of 2.4 mg/L. This ball valve diverted water flow documented. The LLE separation process was conducted
40
toward the filtration media while isolating the reservoir after the samples had completed the distribution phase in
line. The small-scale column test setup was designed to the laboratory-scale water distribution model. A separatory
simulate pilot- or full-scale fixed-bed GAC and sand filters. funnel was used, and a 1:2 solute-to-solvent ratio was
The rapid column test was conducted to evaluate the maintained. In this case, the solutes were THMs and THAAs,
adsorption efficiency of GAC and the filtration capacity and the solvent was ethyl acetate. The extraction began by
of sand media. The carbon fraction used had a particle partially combining the solute and solvent, followed by
size of 170–230 mesh (mean diameter: 76 µm), and it was vigorous shaking for 5 min. Then, an additional 10 mL of
washed with ultrapure water and dried overnight. The solvent was added, and the mixture was again shaken for
dried carbon was then stored in a desiccator before use. 5 min. This process was repeated 5 times, resulting in the
The GAC column was packed with the prepared GAC extraction of a 100 mL sample using 50 mL of solvent, with
particles. The minimum velocity was calculated using the 5-min shaking intervals after each addition. After extraction,
Reynolds number (Re_min), and according to the US EPA/ the separatory funnel formed two distinct layers. The water
Chromium Manual, the recommended range to maintain layer was removed using a funnel dropper, leaving behind
laminar flow is Re = 0.5–1.0. 39 the solvent layer containing the extracted compounds.
The physical characteristics of GAC were determined To determine THMs and THAAs, as recommended
34
according to the American Society for Testing and Materials by EPA Method 555.1, GC-MS (ECD) analysis was
(ASTM) standard test methods, including: moisture conducted using a GCMS-5977B system (Agilent
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 5 doi: 10.36922/EER025240047