Page 99 - EER-2-3
P. 99
Explora: Environment
and Resource Comparative analysis of THMs and THAAs in water distribution media
Figure 5. Chromatogram of the high-density polyethylene pipe water sample treated with a 2.4 mg/L chlorine dosage
A B
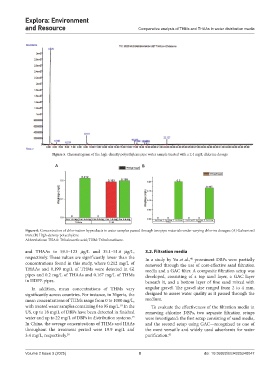
Figure 6. Concentration of chlorination byproducts in water samples passed through two pipe materials under varying chlorine dosages: (A) Galvanized
iron; (B) High-density polyethylene
Abbreviations: THAA: Trihaloacetic acid; THM: Trihalomethane.
and THAAs to 59.5–123 µg/L and 35.1–51.6 µg/L, 3.2. Filtration media
respectively. These values are significantly lower than the In a study by Yu et al., prominent DBPs were partially
40
concentrations found in this study, where 0.212 mg/L of removed through the use of cost-effective sand filtration
THAAs and 0.199 mg/L of THMs were detected in GI media and a GAC filter. A composite filtration setup was
pipes and 0.2 mg/L of THAAs and 0.167 mg/L of THMs developed, consisting of a top sand layer, a GAC layer
in HDPE pipes. beneath it, and a bottom layer of fine sand mixed with
In addition, mean concentrations of THMs vary angular gravel. The gravel size ranged from 2 to 4 mm,
significantly across countries. For instance, in Nigeria, the designed to assess water quality as it passed through the
mean concentrations of THMs range from 0 to 1000 mg/L, medium.
with treated water samples containing 0 to 95 mg/L. In the To evaluate the effectiveness of the filtration media in
18
US, up to 18 mg/L of DBPs have been detected in finished removing chlorine DBPs, two separate filtration setups
water and up to 22 mg/L of DBPs in distribution systems. were investigated: the first setup consisting of sand media,
19
In China, the average concentrations of THMs and HAAs and the second setup using GAC—recognized as one of
throughout the treatment period were 19.9 mg/L and the most versatile and widely used adsorbents for water
3.4 mg/L, respectively. 20 purification. 41
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2025) 8 doi: 10.36922/EER025240047