Page 60 - GHES-1-2
P. 60
Global Health Econ Sustain Antimicrobial eco-friendly material
Figure 7. Thermogravimetric analysis thermograms of the samples. Experiments were run up to 800°C under a nitrogen atmosphere and at a heating rate
of 10°C/min. The Y1 axis corresponds to the loss in weight, and the Y2 axis corresponds to the derivative of weight with respect to temperature (X-axis).
with Ag were a TD displacement from 166.8 to 293.2°C and
a higher residue weight percentage, which is consistent and
can be attributed to metal loading (Figure 7).
3.6. Antimicrobial tests
Kirby-Bauer tests were conducted to evaluate the
antimicrobial properties of the tested materials. Two
bacterial cultures, S. aureus (Gram-positive bacteria)
and P. aeruginosa (Gram-negative bacteria), were used in
these assays. S. aureus (Idrees et al., 2021) has spherical
morphology and aerobic metabolism (although it can
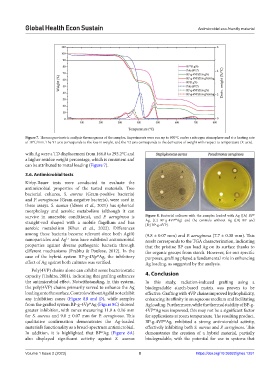
survive in anaerobic conditions), and P. aeruginosa is Figure 8. Bacterial cultures with the samples loaded with Ag ([A] BP @
@
straight-rod shaped with a mobile flagellum and has Ag, [C] BP-g-4VP Ag) and the controls without Ag ([B] BP and
[D] BP-g-4VP).
aerobic metabolism (Khan et al., 2022). Differences
among these bacteria become relevant since both Ag(0) (9.8 ± 0.07 mm) and P. aeruginosa (7.7 ± 0.38 mm). This
nanoparticles and Ag ions have exhibited antimicrobial result corresponds to the TGA characterization, indicating
1+
properties against diverse pathogenic bacteria through that the pristine BP can load Ag on its surface thanks to
different mechanisms (Prabhu & Poulose, 2012). In the the organic groups from starch. However, for our specific
case of the hybrid system BP-g-4Vp Ag, the inhibitory purposes, grafting played a fundamental role in enhancing
@
effect of Ag against both cultures was verified. Ag loading, as suggested by the analysis.
Poly(4VP) chains alone can exhibit some bacteriostatic
capacity (Tashiro, 2001), indicating that grafting enhances 4. Conclusion
the antimicrobial effect. Notwithstanding, in this system, In this study, radiation-induced grafting using a
the poly(4VP) chains primarily served to enhance the Ag biodegradable starch-based matrix was proven to be
loading onto the surface. Controls without Ag did not exhibit effective. Grafting with 4VP chains improved hydrophilicity,
any inhibition zones (Figure 8B and D), while samples enhancing its affinity in an aqueous medium and facilitating
from the grafted system BP-g-4Vp Ag (Figure 8C) showed Ag loading. Furthermore, while the thermal stability of BP-g-
@
greater inhibition, with zones measuring 11.9 ± 0.16 mm 4VP Ag was improved, this may not be a significant factor
@
for S. aureus and 9.8 ± 0.07 mm for P. aeruginosa. This for applications at room temperature. The resulting product,
qualitative confirmation demonstrates the Ag-loaded BP-g-4VP Ag, exhibited a strong antimicrobial activity,
@
material’s functionality as a broad-spectrum antimicrobial. effectively inhibiting both S. aureus and P. aeruginosa. This
In addition, it is highlighted that BP Ag (Figure 8A) demonstrates the creation of a hybrid material, partially
@
also displayed significant activity against S. aureus biodegradable, with the potential for use in systems that
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2023) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/ghes.1251