Page 58 - GPD-2-3
P. 58
Gene & Protein in Disease SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants in Iraq
A B
C
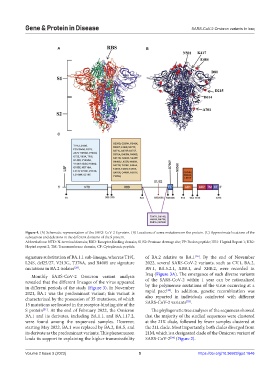
Figure 4. (A) Schematic representation of the SARS-CoV-2 S protein. (B) Locations of some mutations on the protein. (C) Approximate locations of the
substations and deletions in the different domains of the S protein.
Abbreviations: NTD: N-terminal domain; RBD: Receptor-binding domain; S1/S2: Protease cleavage site; FP: Fusion peptide; HR1: Heptad Repeat 1; HR2:
Heptad repeat 2; TM: Transmembrane domain; CP: Cytoplasmic peptide.
signature substitution of BA.1.1 sub-lineage, whereas T19I, of BA.2 relative to BA.1 . By the end of November
[26]
L24S, del25/27, V213G, T376A, and R408S are signature 2022, several SARS-CoV-2 variants, such as CV.1, BA.2,
mutations in BA.2 isolates . BN.1, BA.5.2.1, XBB.1, and XBB.2, were recorded in
[26]
Monthly SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant analysis Iraq (Figure 3A). The emergence of such diverse variants
revealed that the different lineages of the virus appeared of the SARS-CoV-2 within 1 year can be rationalized
in different periods of the study (Figure 3). In November by the polymerase mutations of the virus occurring at a
[32]
2021, BA.1 was the predominant variant; this variant is rapid pace . In addition, genetic recombination was
characterized by the possession of 35 mutations, of which also reported in individuals coinfected with different
[33]
15 mutations are located in the receptor-binding site of the SARS-CoV-2 variants .
S protein . At the end of February 2022, the Omicron The phylogenetic tree analyses of the sequences showed
[31]
BA.1 and its derivates, including BA.1.1, and BA.1.17.2, that the majority of the studied sequences were clustered
were found among the sequenced samples. However, at the 21K clade, followed by fewer samples clustered at
starting May 2022, BA.1 was replaced by BA.2, BA.5, and the 21L clade. Most importantly, both clades diverged from
its derivate as the predominant variants. This phenomenon 21M, which is a designated clade of the Omicron variant of
lends its support in explaining the higher transmissibility SARS-CoV-2 (Figure 2).
[34]
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 5 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.1646