Page 59 - GPD-2-3
P. 59
Gene & Protein in Disease SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants in Iraq
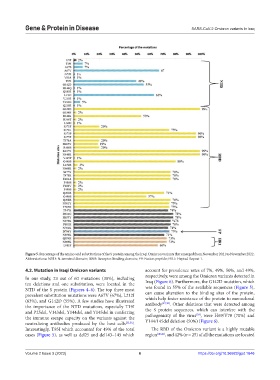
Figure 5. Percentage of the amino acid substitutions of the S protein among the Iraqi Omicron variants that emerged from November 2021 to November 2022.
Abbreviations: NTD: N-terminal domain; RBD: Receptor-binding domain; FP: Fusion peptide; HR1: Heptad Repeat 1.
4.2. Mutation in Iraqi Omicron variants account for prevalence rates of 7%, 49%, 50%, and 49%,
In our study, 23 out of 60 mutations (38%), including respectively, were among the Omicron variants detected in
ten deletions and one substitution, were located in the Iraq (Figure 6). Furthermore, the G142D mutation, which
NTD of the S protein (Figures 4–6). The top three most was found in 55% of the available sequences (Figure 5),
prevalent substitution mutations were A67V (67%), L212I can cause alteration to the binding sites of the protein,
(63%), and G142D (55%). A few studies have illustrated which help foster resistance of the protein to monoclonal
[37,38]
the importance of the NTD mutations, especially T19I antibody . Other deletions that were detected among
and P25del, V143del, Y144del, and Y145del in conferring the S protein sequences, which can interfere with the
[39]
the immune escape capacity on the variants against the pathogenicity of the virus , were H69/V70 (70%) and
neutralizing antibodies produced by the host cells [35,36] . Y144/145del deletion (50%) (Figure 6).
Interestingly, T95I which accounted for 49% of the total The RBD of the Omicron variant is a highly mutable
cases (Figure 5), as well as del25 and del143–145 which region [40,41] , and 42% (n = 25) of all the mutations are located
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.1646