Page 55 - GPD-2-3
P. 55
Gene & Protein in Disease SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants in Iraq
kbp that encodes for a number of accessory proteins and classification. Mutations of each S protein sequences were
four major structural proteins, such as spike (S) protein, identified by manual checking of the recorded sequence
nucleocapsid (N) protein, membrane protein (M), and data, and the sequences were aligned with the first
envelope (E) protein [11-13] . Comprising 1273 amino acids, S sequence of SARS-CoV-2 isolate from Wuhan Hu-1/China
protein is a trimeric protein having several domains that are (accession number: NC_045512.2).
known to facilitate the entry of the virus into the host cells
through the attachment and fusion into the angiotensin- 2.3. Protein visualization and construction of the
converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptor of the host cells . phylogenic trees
[14]
On completing the genetic sequencing of the virus for the Data regarding the 3D structure of the S protein and its
first time, several variants of the virus with varying levels of common mutation sites were obtained the ViralZone
[22]
pathogenicity and transmissibility were reported around the database (https://viralzone.expasy.org/) . A phylogenic
[15]
world . The Omicron variant (B.1.1.529 lineage) was first tree was constructed based on the 381 Omicron variants
identified in Botswana and South Africa on November 24, sequences using the Nextstrain tool (https://nextstrain.
[23]
2021 and then classified as a variant of concern (VOC) on org/) .
November 26, 2021 [16,17] . This variant is characterized by high 3. Results
environmental durability, high transmissibility, firm binding
to human ACE2 receptor, attenuated viral replication, and 3.1. Pango lineage
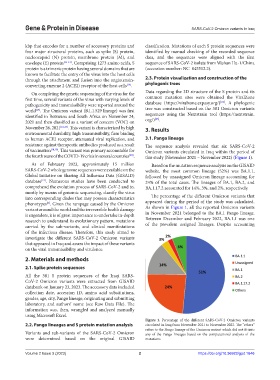
resistance against therapeutic antibodies produced as a result The sequence analysis revealed that six SARS-CoV-2
of vaccination [18,19] . This variant was primary accountable for Omicron variants circulated in Iraq within the period of
the fourth wave of the COVID-19 crisis in several countries . this study (November 2021 – November 2022) (Figure 1).
[20]
As of February 2023, approximately 15 million Based on the mutation sequence analysis on the GISAID
SARS-CoV-2 whole genome sequences were available on the website, the most common lineage (52%) was BA.1.1,
Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data (GISAID) followed by unassigned Omicron lineage accounting for
database . Numerous studies have been conducted to 24% of the total cases. The lineages of BA.1, BA.2, and
[21]
comprehend the evolution process of SARS-CoV-2 and to, BA.1.17.2 accounted for 14%, 3%, and 2%, respectively.
mostly by means of genomic sequencing, classify the virus
into corresponding clades that may possess characteristics The percentage of the different Omicron variants that
phenotypes . Given the rampage caused by the Omicron appeared during the period of the study was calculated.
[6]
variant around the world and the irreversible health damage As shown in Figure 1, all the reported Omicron variants
it engenders, it is of great importance to undertake in-depth in November 2021 belonged to the BA.1 Pango lineage.
research to understand its evolutionary pattern, mutations Between December and February 2022, BA.1.1 was one
carried by the sub-variants, and clinical manifestations of the prevalent assigned lineages. Despite accounting
of the infectious disease. Therefore, this study aimed to
investigate the different SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants
that appeared in Iraq and assess the impact of these variants
on the viral transmissibility and virulence.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Spike protein sequences
All the 381 S protein sequences of the Iraqi SARS-
CoV-2 Omicron variants were extracted from GISAID
databank on January 23, 2023. The accessory data included
collection date, accession ID, amino acid substitutions,
gender, age, city, Pango lineage, originating and submitting
laboratory, and authors’ name (see Raw Data File). The
information was, then, wrangled and analyzed manually
using Microsoft Excel.
Figure 1. Percentage of the different SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants
2.2. Pango lineages and S protein mutation analysis circulated in Iraq from November 2021 to November 2022. The “others”
refers to the Pango lineage of the Omicron variant which did not fit into
Variants and sub-variants of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron any of the Pango lineages based on the computational analysis of the
were determined based on the original GISAID mutations.
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 2 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.1646