Page 160 - GPD-4-1
P. 160
Gene & Protein in Disease FXR1 modulates gene expression in cancer
B
C
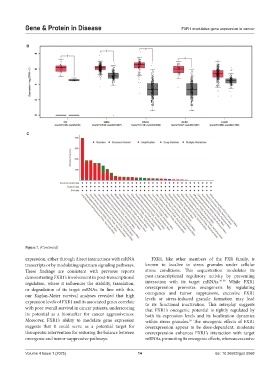
Figure 7. (Continued)
expression, either through direct interactions with mRNA FXR1, like other members of the FXR family, is
transcripts or by modulating upstream signaling pathways. known to localize to stress granules under cellular
These findings are consistent with previous reports stress conditions. This sequestration modulates its
demonstrating FXR1’s involvement in post-transcriptional post-transcriptional regulatory activity by preventing
regulation, where it influences the stability, translation, interaction with its target mRNAs. 36-38 While FXR1
or degradation of its target mRNAs. In line with this, overexpression promotes oncogenesis by regulating
our Kaplan-Meier survival analyses revealed that high oncogenes and tumor suppressors, excessive FXR1
levels or stress-induced granule formation may lead
expression levels of FXR1 and its associated genes correlate to its functional inactivation. This interplay suggests
with poor overall survival in cancer patients, underscoring that FXR1’s oncogenic potential is tightly regulated by
its potential as a biomarker for cancer aggressiveness. both its expression levels and its localization dynamics
Moreover, FXR1’s ability to modulate gene expression within stress granules. The oncogenic effects of FXR1
39
suggests that it could serve as a potential target for overexpression appear to be dose-dependent; moderate
therapeutic intervention for restoring the balance between overexpression enhances FXR1’s interaction with target
oncogenic and tumor-suppressive pathways. mRNAs, promoting its oncogenic effects, whereas excessive
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 14 doi: 10.36922/gpd.5068