Page 47 - GTM-1-2
P. 47
Global Translational Medicine Cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma
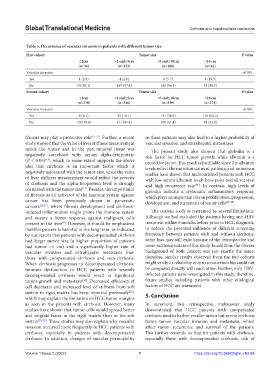
Table 5. Occurrence of vascular invasion in patients with different tumor size
First cohort Tumor size P‑value
≤2cm >2 and≤5cm >5 and≤10cm >10 cm
(n=34) (n=153) (n=106) (n=41)
Vascular invasion <0.001
Yes 1 (2.9) 4 (2.6) 6 (5.7) 8 (19.5)
No 33 (97.1) 149 (97.4) 100 (94.3) 33 (80.5)
Second cohort Tumor size P‑value
≤2cm >2 and≤5cm >5 and≤10cm >10 cm
(n=128) (n=346) (n=339) (n=274)
Vascular invasion <0.001
Yes 8 (6.2) 35 (10.1) 131 (38.6) 176 (64.2)
No 120 (93.8) 311 (89.9) 208 (61.4) 98 (35.8)
fibrosis may play a protective role [15-17] . Further, a recent in these patients may also lead to a higher probability of
study showed that the value of liver stiffness measurement vascular invasion and extrahepatic metastases.
inside the tumor and in the peri-tumoral tissue was The present study also showed that globulin is a
negatively correlated with serum alpha-fetoprotein risk factor for HCC tumor growth, while albumin is a
(P < 0.05) , which to some extent supports the above protective factor. This result is justifiable since the albumin
[18]
idea that cirrhosis is an important factor which is levels reflect the nutrition status of patients, and numerous
negatively associated with the tumor size, since the value studies have shown that malnourished patients with HCC
of liver stiffness measurement would reflect the severity with low serum albumin levels have poor overall survival
of cirrhosis and the alpha-fetoprotein level is strongly and high recurrence rate . In contrast, high levels of
[26]
correlated with the tumor size . Besides, the importance globulin indicate a systematic inflammatory response,
[19]
of fibrosis as an activator of the immune system against which plays an important role in proliferation, progression,
cancer has been previously shown in pancreatic development, and metastasis of tumor cells [26-28] .
cancers [20,21] , where fibrosis development and cirrhosis-
induced inflammation might prime the immune system The current study is restrained by several limitations.
and ensure a better response against malignant cells Although we had excluded the patients having anti-HBV
present in the liver . However, it should be emphasized treatment within 6 months before prior to HCC diagnosis,
[9]
that this process is harmful in the long term, as indicated to reduce the potential influence of different screening
by our results that patients with decompensated cirrhosis frequency between patients with and without cirrhosis,
had larger tumor size (a higher proportion of patients some bias may still exist because of the retrospective and
had tumor >5 cm) and a significantly higher rate of cross-sectional nature of this study. In addition, the disease
vascular invasion and extrahepatic metastasis than background of both cohorts was not exactly the same;
those with compensated cirrhosis and non-cirrhosis. therefore, similar results observed from the two cohorts
When cirrhosis progresses to decompensated cirrhosis, might verify its reliability only to some extent but could not
immune dysfunction in HCC patients with severely be compared directly with each other. Further, only HBV-
decompensated cirrhosis would result in significant infected patients were investigated in this study; therefore,
tumor growth and metastasis . Decreased efficiency of future studies including patients with other etiological
[13]
cell durotaxis and increased level of stiffness from soft factors of HCC are warranted.
matrix to rigid matrix has been reported previously ,
[22]
which may explain the limitation on HCC tumor margins 5. Conclusion
as seen in the patients with cirrhosis. However, many In summary, this retrospective multicenter study
studies have shown that tumor cells would spread better demonstrated that HCC patients with compensated
and migrate faster in the rigid matrix than in the soft cirrhosis tend to harbor smaller tumor but severe cirrhosis
matrix [23-25] . These studies may also explain why vascular favors tumor vascular invasion and metastasis, which
invasion occurred more frequently in HCC patients with affect tumor recurrence and survival of the patients.
cirrhosis, especially in patients with decompensated This further reminds us that for patients with cirrhosis,
cirrhosis. In addition, changes of vascular permeability especially those with decompensated cirrhosis, risk of
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 7 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v1i2.94