Page 52 - GTM-1-2
P. 52
Global Translational Medicine A Taxonomy of AI Assisted Medical Robots
These standard procedures could be learned through
AI-ART . Wang et al. developed a medical robot
[56]
[56]
system equipped with stereo vision, incision detection,
and staple positioning algorithms for surgical suturing and
staples removals. Lu et al. presented an in-house vision
[54]
system with efficient trajectory planning algorithms. They
successfully addressed the automatic suturing problem
with two collaborative grippers through visual detection
algorithms, which also eliminated the risk of collisions
between the two gripers. In fact, their work does not
include the full automation of medical robots, but rather
only as a sub-state semi-automatic assistant for surgeons.
Moreover, the tactile sensation between the operated tissue
or organ and the robotic gripper does not provide any
feedback to the surgeons or have a monitoring module of
the computer unit.
Even with artificial intelligence assistance for
laparoscopic surgery, full-automation medical robots have
not been approved by the Food and Drug Administration
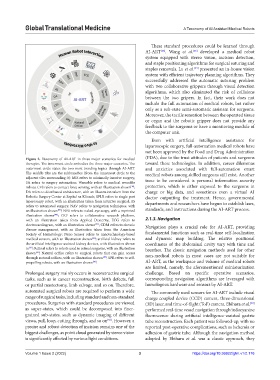
Figure 2. Taxonomy of AI-ART in three major scenarios for medical (FDA), due to the trust attitudes of patients and surgeons
therapies. The innermost circle embodies the three major scenarios. The toward these technologies. In addition, career dilemmas
outermost circle states the two most trending topics through AI-ART. and anxieties associated with full-automation smart
The middle tiles are the subbranches (from the innermost circle to the medical robots among skilled surgeons still exist. Another
adjacent tiles surrounding it): MIS refers to minimally invasive surgery;
SA refers to surgery automation; Wearable refers to medical wearable issue to be considered is personal information security
robots; CFS refers to contact force sensing, with an illustration shown ; protection, which is either exposed to the surgeons in
[38]
DA refers to distributed architecture, with an illustration taken from the charge or big data, and sometimes even a virtual AI
Robotic Surgery Center at Szpital na Klinach; SPLR refers to single port doctor outputting the treatment. Hence, governmental
laparoscopy robot, with an illustration taken from intuitive surgical; AS departments and researchers have begun to establish laws,
refers to automated surgery; NAV refers to navigation techniques, with
an illustration shown ; NES refers to naked-eye scopy, with a reprinted standards, and instructions during the AI-ART process.
[39]
illustration shown ; CRP refers to collaborative research platform,
[40]
with an illustration taken from Applied Dexterity; ECG refers to 2.1.3. Navigation
electrocardiogram, with an illustration shown ; CDM refers to chronic Navigation plays a crucial role for AI-ART, providing
[41]
disease management, with an illustration taken from the American
Society of Hematology; Nano Sensor refers to nanotechnology-based fundamental functions such as real-time self-localization
medical sensors, with an illustration shown ; artificial kidney refers to and dynamic map building. The relative positional
[42]
the artificial intelligence-assisted kidney devices, with illustration shown coordinates of the abdominal cavity vary with time and
in ; Retinal refers to robots used in retinal surgeries, with an illustration breathes. The classic navigation methods used for other
[43]
shown ; Natural orifice refers to surgical robots that can gain access
[44]
through natural orifices, with an illustration shown ; SPR refers to self- non-medical robots in most cases are not suitable for
[45]
propelling robots, with an illustration shown . AI-ART, as the workspace and volume of medical robots
[46]
are limited, namely, the aforementioned miniaturization
Prolonged surgery mainly occurs in reconstructive surgical challenge. Based on specific operative scenarios,
tasks, such as in cancer reconstruction, birth defects, full corresponding navigation algorithms are leveraged with
or partial mastectomy, limb salvage, and so on. Therefore, homologous hardware and sensors by AI-ART.
automated surgical robots are required to perform a wide The commonly used sensors for AI-ART include visual
range of surgical tasks, including standard and non-standard charge coupled device (CCD) camera, three-dimensional
procedures. Surgeries with standard procedures are viewed (3D) laser, and time-of-flight (ToF) camera. Ebihara et al.
[39]
as super-states, which could be decomposed into finer- performed real-time vessel navigation through indocyanine
grained sub-states, such as dynamic imaging of different fluorescence during artificial intelligence-assisted gastric
views, pull, loop, cutting through, and so on . However, a tube reconstruction. Each patient was followed-up, with no
[56]
precise and robust detection of incision remains one of the reported post-operative complications, such as ischemia or
biggest challenges, as point cloud generated by stereo vision adhesion of gastric tube. Although the navigation method
is significantly affected by various light conditions. adopted by Ebihara et al. was a classic approach, they
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 3 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v1i2.176