Page 53 - GTM-1-2
P. 53
Global Translational Medicine A Taxonomy of AI Assisted Medical Robots
A B
C D E
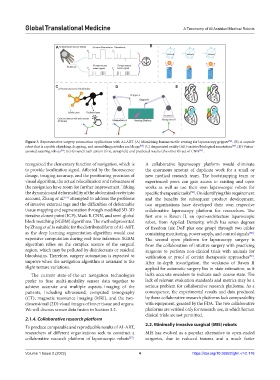
Figure 3. Representative surgery automation applications with AI-ART. (A) Mimicking human tactile sensing for laparoscopy gripper . (B) A capsule
[50]
robot that is capable of picking, dropping, and assembling particles and drugs . (C) Augmented reality (AR)-assisted biological annotation . (D) Vision-
[52]
[53]
assisted suturing robots . (E) Ground truth atrium (first, at top left) and predicted results (the other three) of CNN .
[54]
[55]
recognized the elementary function of navigation, which is A collaborative laparoscopy platform would eliminate
to provide localization signal. Affected by the fluorescence the enormous amount of duplicate work for a small or
dosage, imaging accuracy, and the positioning precision of new medical research team. The bootstrapping team or
visual algorithm, the actual relocalization and robustness of experienced peers can gain access to existing and open
the navigation have room for further improvement. Taking works as well as use their own laparoscopic robots for
the dynamics and deformability of the abdominal cavity into specific therapeutic tasks . On identifying this requirement
[58]
account, Zhang et al. attempted to address the problems and the benefits for subsequent product development,
[57]
of invasive external tags and the difficulties of deformable two organizations have developed their own respective
tissue mapping and segmentation through modified 3D-3D collaborative laparoscopy platform for researchers. The
iterative closest point (ICP), Mask R-CNN, and semi-global first one is Raven II, an open-architecture laparoscopic
block matching (SGBM) algorithms. The method presented robot, from Applied Dexterity, which has seven degrees
by Zhang et al. is suitable for the distributed form of AI-ART, of freedom (six DoF plus one grasp) through two cables
as the deep learning segmentation algorithm would cost containing monitoring, power supply, and control signals .
[58]
expensive computation during real-time inference. SGBM The second open platform for laparoscopy surgery is
algorithm relies on the complex texture of the surgical from the collaboration of intuitive surgery with practicing
region, which may be polluted by disinfectants or residual surgeons to perform non-clinical trials with animals for
bloodstains. Therefore, surgery automation is expected to verification or proof of certain therapeutic approaches .
[59]
improve when the navigation algorithm is invariant to the After in-depth investigation, the weakness of Raven II
slight texture variations. applied for automatic surgery lies in state estimation, as it
The current state-of-the-art navigation technologies lacks accurate encoders to indicate each coarse state. The
prefer to fuse multi-modality sensor data together to lack of relevant evaluation standards and metrics may be a
achieve accurate and multiple aspects imaging of the serious problem for collaborative research platforms. As a
patients, including ultrasound, computed tomography consequence, the experimental results and data produced
(CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and the two- by these collaborative research platforms lack comparability
dimensional (2D) visual images of inner tissue and organs. with equipment, granted by the FDA. The two collaborative
We will discuss sensor data fusion in Section 3.2. platforms are verified only for research use, in which human
clinical trials are not permitted.
2.1.4. Collaborative research platform
2.2. Minimally invasive surgical (MIS) robots
To produce comparable and reproducible results of AI-ART,
researchers of different organizations seek to construct a MIS has evolved as a popular alternative to open-ended
collaborative research platform of laparoscopic robots . surgeries, due to reduced trauma and a much faster
[57]
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 4 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v1i2.176