Page 57 - GTM-1-2
P. 57
Global Translational Medicine A Taxonomy of AI Assisted Medical Robots
a wearable artificial kidney, the patient may not have access 3.1. Feedback of tactile sensation
to dialysis storage or caregiver at any time . The application of either classic laparoscopy or AI-ART for
[70]
The main direction is the study of sorbent adsorption, medical robots isolates the surgeon’s tactile sensation from
in which highly effective activated charcoals can inherently the patient’s deformable tissue or skin. However, either
absorb uremic toxins. Historically, the exclusive sorbents the surgical robot with on-site surgeons or telesurgery
system has been proven ineffective in binding and eliminating through 5G communication technologies is required to
urea. Hence, researchers have developed five types of sorbents, hold or pull the tissue with proper force without secondary
to the best of our knowledge, for urea adsorption. One of the classic laparoscopic injury. Researchers have explored new
five types includes TPA-COF (covalent organic framework) sensation technologies for the interaction between medical
nanosheets and TPA-COF nanoparticle modified with -OH, robots and soft tissue . The fundamental work of AI-ART
[76]
which have been verified to have better urea adsorption based for medical robots is undoubtedly the calibration of force
on molecular study. Other directions of wearable artificial sensor or torque sensor, which transforms raw electrical
kidney include enzymatic removal of urea, electro-oxidation, signal into force or torque values with real physical
photo-oxidation, blood compatibility, and human factors . meaning. With regard to the progress of calibration,
[69]
Artificial intelligence-assisted analysis would improve the the main focus is on end-to-end neural networks as the
search for more efficient materials relating to the development multi-axis data and their mutual coupling. Deep learning
of sorbents in three aspects: (1) Effective combination of algorithms have been leveraged for the calibration of force
candidate structures; (2) more reliable dynamics simulation and torque sensors. On the basis of calibration works, the
for liquid circuit system; and (3) accurate prediction of the skin-like sensor that is able to attach to arbitrary surface has
recharge of consumable materials. drawn interests, as it can be manufactured into non-array
3. Human-robot interaction for automation arrangement as well as sense and transmit signals even
with partial damages. Four artificial neural networks have
or telesurgery been adopted to determine their slippage and accuracy data
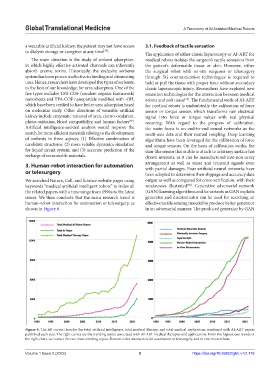
We searched Nature, Cell, and Science website pages using output as well as compared for cross-verification, with their
[50]
keywords “medical artificial intelligent robots” to index all weaknesses illustrated . Generative adversarial network
the related papers with a time range from 1990s to the latest (GAN) learning algorithms and its variants as GAN exploits
issues. We then conclude that the main research trend is generator and discriminator can be used for searching an
human-robot interaction for automation or telesurgery, as effective tactile sensing material to produce better generator
shown in Figure 6. in an adversarial manner. The produced generator by GAN
Figure 6. The left curves describe the total artificial intelligence, total medical therapy, and total medical applications combined with AI-ART papers
published each year. The right curves are the trending topics associated with AI-ART medical therapies and applications. From the highest two trends of
the right chart, we extract the two most trending topics: Human-robot interaction for automation or telesurgery and in vivo microrobots.
Volume 1 Issue 2 (2022) 8 https://doi.org/10.36922/gtm.v1i2.176